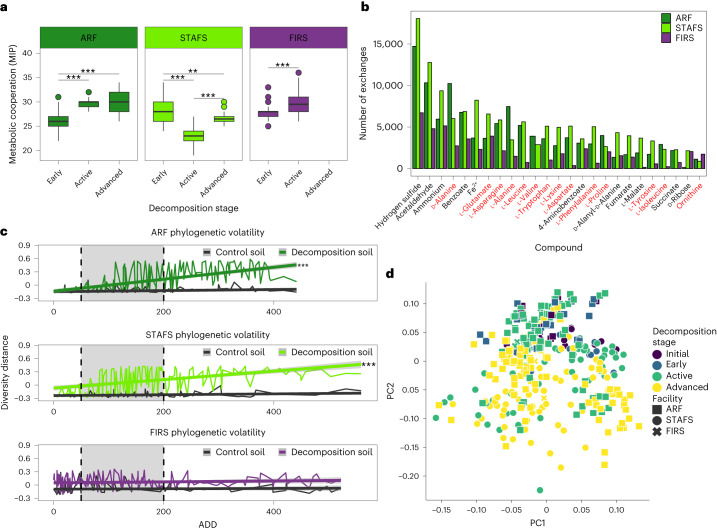
Fig. 3. Decomposition microbial ecology is influenced by microbial interactions and environmental conditions.
a, Predicted cross-feeding interactions from MAGs are site-specific and significantly altered over decomposition. ARF n = 201, STAFS n = 188 and FIRS n = 151 biologically independent samples. In boxplots, the lower and upper hinges correspond to the first and third quartiles (the 25th and 75th percentiles); the upper and lower whiskers extend from the hinge to the largest and smallest values no further than 1.5× IQR; the centre lines represent the median. Significance was tested with Dunn Kruskal–Wallis H-test, with multiple-comparison P values adjusted with the Benjamini–Hochberg method. ARF early-active P = 1.95 × 10−23, early-advanced P = 1.67 × 10−23; STAFS early-active P = 5.53 × 10−39, early-advanced P = 3.65 × 10−03, active-advanced P = 2.04 × 10−24; FIRS early-active P = 3.81 × 10−15. b, Increased cross-feeding reactions during semi-arid active decomposition and temperate advanced decomposition are summarized to show that compounds such as amino acids (red) are common among the top 25 potential cross-fed molecules from MAGs. c, Phylogenetic turnover in decomposition soil vs control soil shows that temperate climates react quickly to decomposition, while the more arid site does not quickly change (dashed lines represent breaks for early, active (grey shading) and advanced decomposition stages) using the 16S rRNA gene amplicon dataset. ARF n = 414, STAFS n = 316 and FIRS n = 310 biologically independent samples. Data are presented as mean ± 95% CI. Significance was tested using linear mixed-effects models within each location, including a random intercept for cadavers with two-tailed ANOVA and no multiple-comparison adjustments. ARF and STAFS richness P ≤ 2 × 10−16. d, Multi-omic (16S rRNA gene abundances, 18S rRNA gene abundances, MAG abundances, MAG gene abundances, MAG gene functional modules and metabolites) joint-RPCA shows that microbial community ecology is impacted by decomposition stage and geographical location. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001.