Table S1. Comparison of clinical characteristics of GEPNEC and digestive adenocarcinoma.
| Characteristics | n (%) | P | |
| GEPNEC (N=99) | Digestive adenocarcinoma (N=101) | ||
| GEPNEC, gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine carcinoma; SCNEC, small-cell NEC; LCNEC, large-cell NEC; MiNEN, mixed neuroendocrine-non-neuroendocrine neoplasia; NSE, neuron-specific enolase. #, one NEC patients had difficulty in identifying small or large cell subtypes. | |||
Age (year) (
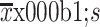 )
)
|
59.6±12.2 | 60.3±11.7 | 0.532 |
| Gender | 0.451 | ||
| Female | 36 (36.4) | 43 (42.6) | |
| Male | 63 (63.6) | 58 (57.4) | |
| Primary sites | − | ||
| Bile duct | 8 (8.1) | 7 (6.9) | |
| Colorectum | 18 (18.2) | 56 (55.4) | |
| Duodenum | 9 (9.1) | − | |
| Esophagus | 7 (7.1) | − | |
| Stomach | 32 (32.3) | 26 (25.7) | |
| Pancreas | 12 (12.1) | 12 (11.9) | |
| Unknown primary | 13 (13.1) | − | |
| Pathology # | − | ||
| Undistinguishable | 1 (1.0) | − | |
| LCNEC | 43 (43.4) | − | |
| SCNEC | 55 (55.6) | − | |
| Adenocarcinoma | − | 101 (100) | |
| Mixed component | − | ||
| MiNEN | 17 (17.2) | − | |
| Pure NEC | 82 (82.8) | − | |
| Stage | <0.001 | ||
| Stage I−III | 17 (17.2) | 61 (60.4) | |
| Stage IV | 82 (82.8) | 40 (39.6) | |
| Metastases | 0.166 | ||
| Liver | 58 (58.6) | 27 (26.7) | |
| Lung | 12 (12.1) | 7 (6.9) | |
| Bone | 9 (9.1) | 3 (3.0) | |
| NSE elevation | <0.001 | ||
| No | 34 (34.3) | 72 (71.3) | |
| Yes | 65 (65.7) | 29 (28.7) | |
| Smoking | 0.446 | ||
| No | 79 (79.8) | 75 (74.3) | |
| Yes | 20 (20.2) | 26 (25.7) | |
