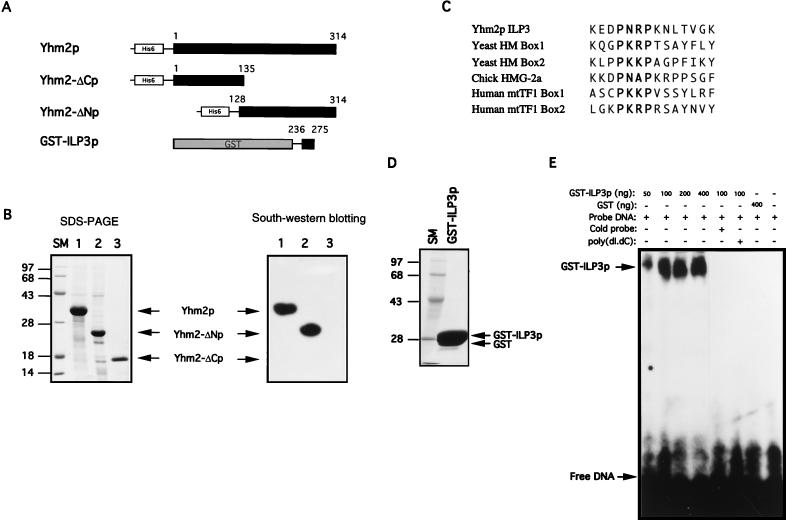
FIG. 5.
DNA-binding ability of Yhm2p. (A) Construction of plasmids for expression of full-length and partial fragments of Yhm2p. A hexahistidine peptide sequence was placed at the amino terminus for affinity purification of the protein. For expression of a short segment of ILP3 (from 236 to 275 of Yhm2p [Fig. 3]), the ILP3 sequence was fused with GST. (B) Coomassie blue staining pattern of the proteins purified by affinity chromatography as described in Materials and Methods (left). DNA binding to the proteins immobilized on a nitrocellulose membrane (right). The purified recombinant proteins were fractionated by PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose membrane. The immobilized protein was refolded in situ and probed with 32P-labeled DNA as described in Materials and Methods. DNA bound to full-length Yhm2p and the carboxy-terminal half of the protein (Yhm2-ΔNp) but not to the amino-terminal half (Yhm2-ΔCp). (C) The amino-acid sequence of ILP3 of Yhm2p is similar to the amino-terminal sequences of various HMG boxes. The proline repeat in bold is important for the DNA-binding activity of the HMG box. (D) Coomassie blue staining of the purified recombinant GST-ILP3 protein. (E) DNA-binding activity of the ILP3 region. DNA binding to the ILP3 region was demonstrated by a DNA mobility shift assay as described in Materials and Methods.