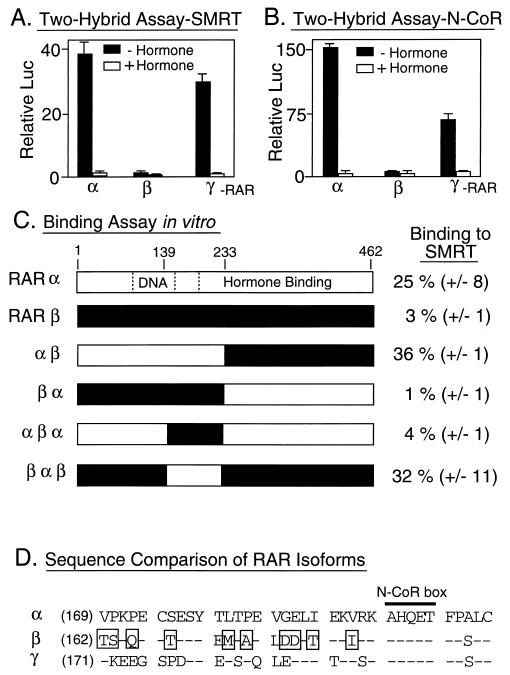
FIG. 5.
Different RAR isoforms differ in their abilities to interact with SMRT. (A) Interactions of different RAR isoforms with SMRT, as determined with a mammalian two-hybrid assay in vivo. RARα, RARβ, and RARγ were expressed as GAL4AD fusions in CV-1 cells and tested for the ability to interact with GAL4DBD-SMRT (amino acids 751 to 1495) and induce the expression of the GAL4 (17-mer)-luciferase reporter. The cells were incubated in the absence or presence of cognate hormone; after 48 h, the cells were harvested and luciferase activity was determined relative to that of pCH110, used as an internal control (Relative Luc). The results represent the averages and standard deviations from at least two duplicate experiments. (B) Interactions of different RAR isoforms with N-CoR, as determined with a mammalian two-hybrid assay in vivo. The same assay as that in panel A was performed, but with a GAL4DNA–N-CoR construct in place of the GAL4DBD-SMRT construct. (C) Abilities of RARα, RARβ, or RARα-RARβ chimeras to bind to GST-SMRT in vitro. The different receptors, depicted schematically, were synthesized in vitro and tested for their abilities to bind to GST-SMRT (amino acids 751 to 1495) as described in the legend to Fig. 2. The locations of the DNA-binding and hormone-binding domains are indicated within the RARα schematic. The amount of receptor bound to the immobilized GST-SMRT polypeptide, relative to the input amount of receptor, is indicated numerically to the right of each protein schematic. The averages and standard deviations of two or more determinations are presented. (D) Amino acid sequence comparison of the central domains of RARα, RARβ, and RARγ. The amino acid sequences of the central domains of the human RAR isoforms are presented beginning with the amino acid indicated parenthetically to the left of each sequence. Amino acids in RARβ or RARγ that are identical to those in equivalent positions in RARα are depicted by dashes, whereas amino acids in RARβ that are not conserved in either RARα or RARγ are boxed. The location of an N-CoR box is also shown (see the text).