Fig 1.
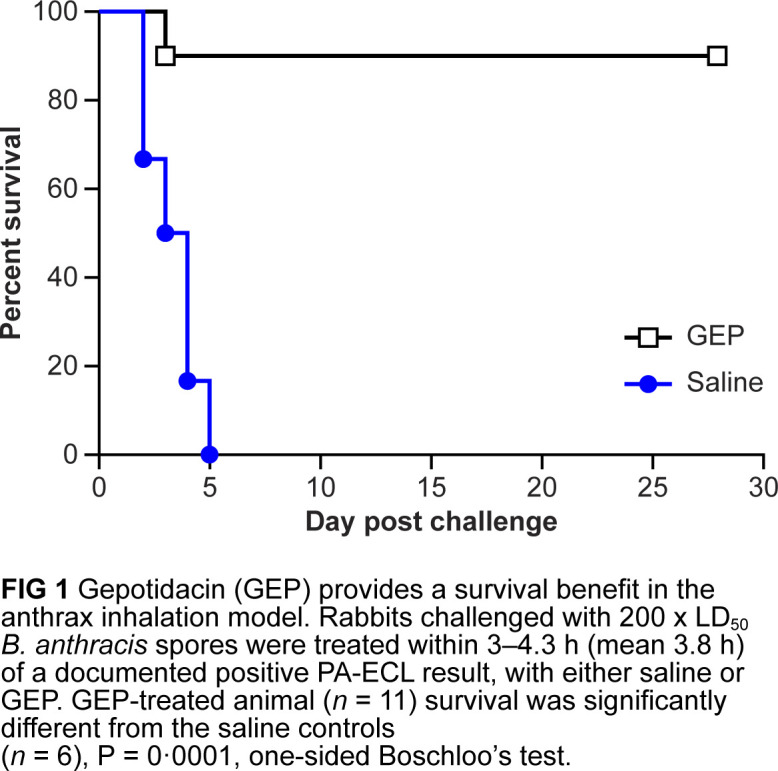
Gepotidacin (GEP) provided a survival benefit in the anthrax inhalation model. Rabbits challenged with 200 x LD50 B. anthracis spores were treated within 3 to 4.3 h (mean 3.8 h) of a documented positive protective antigen electrochemiluminescence result, with either saline or GEP. The survival of GEP-treated animals (n = 11) was significantly different from that of the saline control (n = 6), P = 0.0001, one-sided Boschloo’s test.
