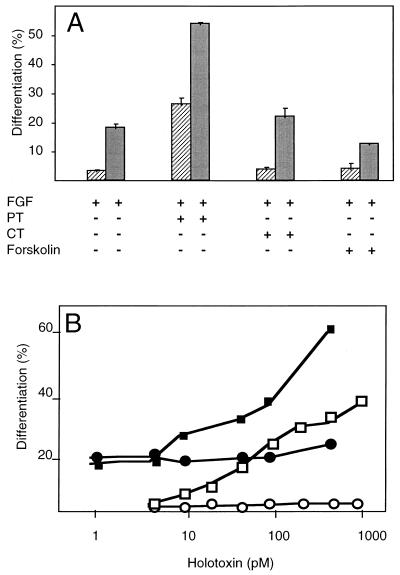
FIG. 1.
PT stimulates skeletal muscle differentiation in the presence of FGF-2. (A) MM14 cells were incubated in the presence of 15% (▨) or 2.5% ( ) serum in medium containing 0.3 nM FGF-2. PT (50 ng/ml; 480 pM), CT (1,000 ng/ml; 11.9 nM), or forskolin (10 μM) was added 1 h after plating. Cells were fixed and stained 48 h after plating. Differentiation of MM14 cells was assayed by clonal analysis as described in Materials and Methods and determined as the number of nuclei in MHC-positive cells. Mean values and standard deviations represent three independent experiments performed in triplicate. No fewer than 75 colonies/100 cells were counted per point per experiment. (B) The B oligomer of pertussis toxin does not affect myogenic differentiation. MM14 cells were incubated in the presence of 15% (□ and ○) or 2.5% (■ and •) serum in medium containing 0.3 nM FGF-2. Cells received the indicated concentrations of holotoxin (■ and □) or B oligomer (• and ○), added at equivalent molar concentrations. Mean values represent the averages of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Standard deviations were no more than 5% for PT in 2.5% serum, 2.4% for PT in 15% serum, 3.3% for B oligomer in 2.5% serum, and 0.5% for B oligomer in 15% serum.
) serum in medium containing 0.3 nM FGF-2. PT (50 ng/ml; 480 pM), CT (1,000 ng/ml; 11.9 nM), or forskolin (10 μM) was added 1 h after plating. Cells were fixed and stained 48 h after plating. Differentiation of MM14 cells was assayed by clonal analysis as described in Materials and Methods and determined as the number of nuclei in MHC-positive cells. Mean values and standard deviations represent three independent experiments performed in triplicate. No fewer than 75 colonies/100 cells were counted per point per experiment. (B) The B oligomer of pertussis toxin does not affect myogenic differentiation. MM14 cells were incubated in the presence of 15% (□ and ○) or 2.5% (■ and •) serum in medium containing 0.3 nM FGF-2. Cells received the indicated concentrations of holotoxin (■ and □) or B oligomer (• and ○), added at equivalent molar concentrations. Mean values represent the averages of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Standard deviations were no more than 5% for PT in 2.5% serum, 2.4% for PT in 15% serum, 3.3% for B oligomer in 2.5% serum, and 0.5% for B oligomer in 15% serum.