FIG. 7.
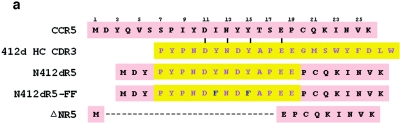
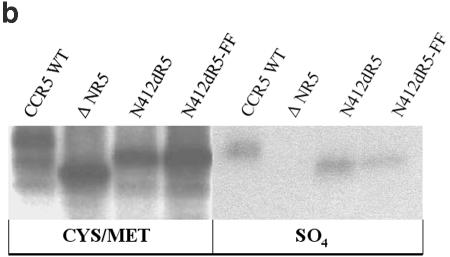
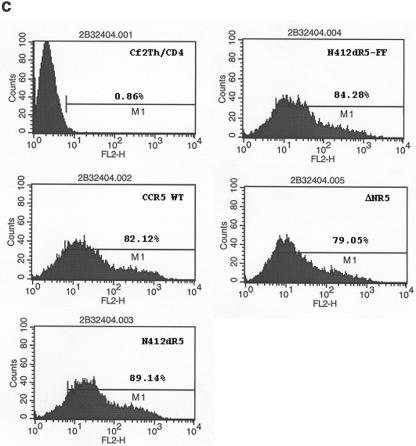
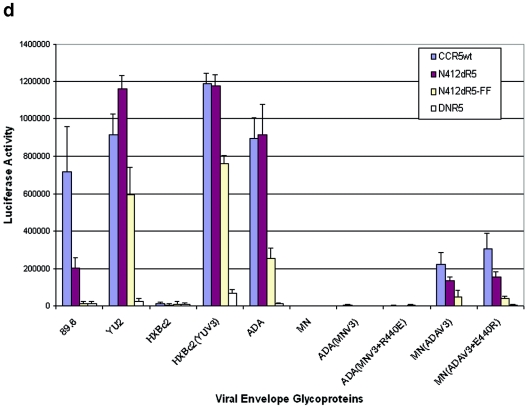
Functional replacement of the CCR5 N terminus with the 412d heavy-chain CDR3 sequence. (a) The sequences of the CCR5 N terminus, the 412d heavy-chain CDR3, and the chimeric receptor constructs are shown. The ΔNR5 mutant has a deletion affecting the N terminus of CCR5. (b) Cf2Th cells expressing the indicated CCR5 variants were radiolabeled with 35S-cysteine/methionine (CYS/MET) or 35S-sulfate (SO4). The lysates were precipitated with the 1D4 antibody directed against the C9 C-terminal epitope tag on the CCR5 variants. Precipitates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. (c) Cf2Th-CD4 cells expressing the indicated CCR5 variants were incubated with phycoerythrin-conjugated 2D7 antibody and analyzed by fluorescence-activated cell sorter. (d) The graph shows the luciferase activity in target Cf2Th-CD4 cells expressing the indicated CCR5 variants, following incubation with recombinant luciferase-expressing HIV-1 containing the indicated HIV-1 envelope glycoproteins. The values shown represent the means and standard deviation of four replicate experiments. Because of the high level of infectivity of the virus with the HXBc2(YUV3) glycoproteins, the values shown represent 1/10 of the actual luciferase activity observed.