Figure 1.
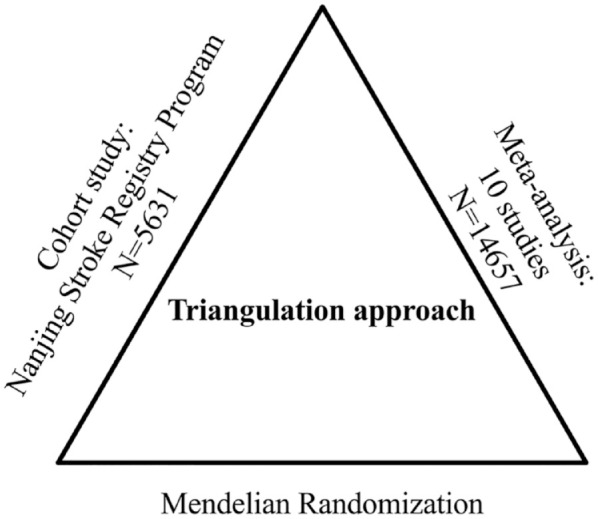
Study design of triangulation approach. A comprehensive three-stage study design was employed to investigate the relationship between uric acid (UA) and stroke prognosis. In the first stage, a large-scale hospital-based prospective registry was used to assess the association between UA and stroke prognosis. In the second stage, a meta-analysis was conducted to consolidate findings from previously published studies on UA and 90-day clinical outcomes, enhancing the overall understanding of the correlation. Finally, in the third stage, Mendelian randomization analysis was performed utilizing summary data from the CKDGen and the Genetics of Ischemic Stroke Functional Outcome Network (GISCOME) to assess whether genetically determined UA was causally linked to stroke functional outcomes.
