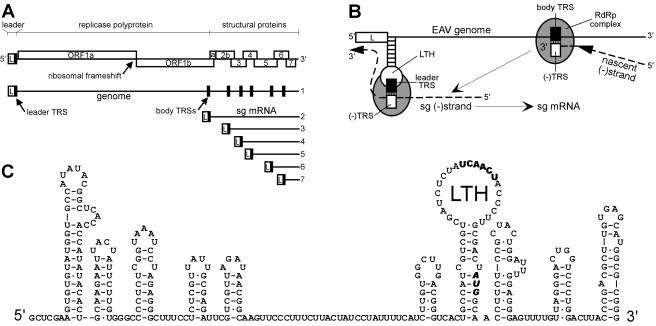
FIG. 1.
(A) Schematic overview of the genome organization and expression of EAV. The replicase gene (ORFs 1a and 1b), the structural protein genes (2a, 2b, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7), and the leader (L) are indicated. The black boxes in the genomic RNA indicate the positions of the leader TRS and (major) body TRSs. A coterminal nested set of sg mRNAs 2 to 7 is depicted below the genome. (B) Discontinuous minus-strand extension model for nidovirus sg RNA synthesis (31). After attenuation of the RdRp complex at a body TRS in the plus-strand genomic template, the nascent strand is translocated to the leader TRS region. Following (−) body TRS to (+) leader TRS base pairing, minus-strand RNA synthesis resumes to add the complement of the leader sequence. Subsequently, the sg minus strand serves as a template for sg mRNA production. (C) RNA secondary-structure model of the 5′-proximal 313 nt of the EAV RNA genome (38). The leader TRS and the replicase translation initiation codon are depicted in boldface.