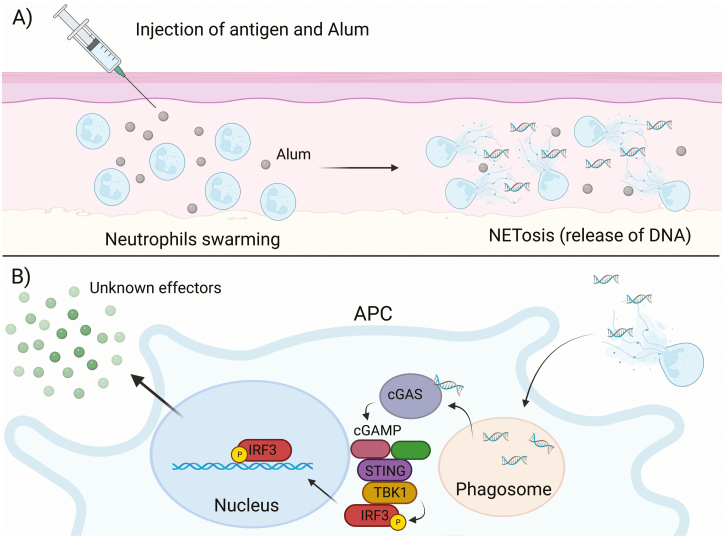
Figure 3:
Alum induces rapid neutrophil swarming and NETosis that activates the cGAS-STING signalling pathway and confers its adjuvant activity. (a) Neutrophils are rapidly recruited to the site of injection and form neutrophil swarms around the deposited alum. The presence of alum induces the recruited neutrophils to undergo rapid NETosis that releases host DNA into the extracellular space. (b) Antigen presenting cells engulf the released NETs and the host DNA that was expelled with them. After exiting the phagosome (facilitated by the neutrophil elastase protein), the DNA is recognised in the cytosol by cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) synthase (cGAS) receptor. cGAS generates cGAMP, which recruits the adaptor protein, stimulator of interferon (IFN) genes (STING). STING recruits TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) which then recruits and phosphorylates IFN regulatory factor 3 (IRF3). Although IRF3 is a known transcription factor responsible for type I IFN production, it is unlikely that alum adjuvant function is dependent of these cytokines, so the final effector responses induced by IRF3 remains unclear. Created with BioRender.com.