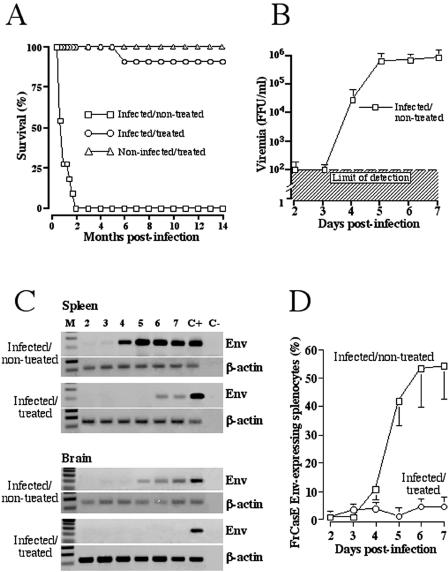
FIG. 1.
In vivo antiviral activity of intraperitoneally injected 667 MAb and infection kinetic analysis. (A) Survival of FrCasE-infected animals. Two groups of ten 3-day-old mice were infected with FrCasE, one of which was treated with 667 and the other not. As a control group, 10 pups were treated with 667 but not infected. (B) Viremia. Thirty 3-day-old animals were infected with FrCasE and half of them were treated with 667 as in A. Two animals per group were sacrificed each day and their sera were pooled for viremia assay by immunofluorescence assay. Infected/ treated animal viremia was below the detection limit. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. (C) Reverse transcription-PCR detection of FrCasE Env mRNA. Spleens and brains were recovered from the same animals as in B. Subgenomic FrCasE Env mRNA accumulation was assayed by reverse transcription-PCR as described in Materials and Methods. β-Actin was used as an internal amplification standard. C+ corresponds to a newborn FrCasE-infected mouse sacrificed 2 weeks postinfection and C- to a negative control with H2O instead of RNA. (D) Expression of cell surface Env in splenocytes. Splenocytes from mice infected in (B) were analyzed by flow cytometry for expression of cell surface-expressed Env. Values are the results of 2 experiments performed in triplicate and are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean.