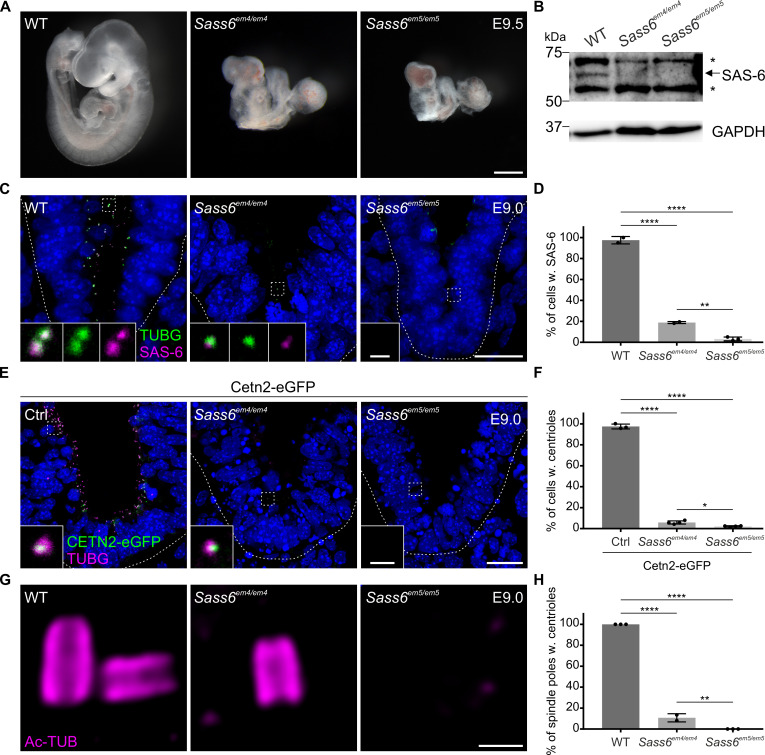
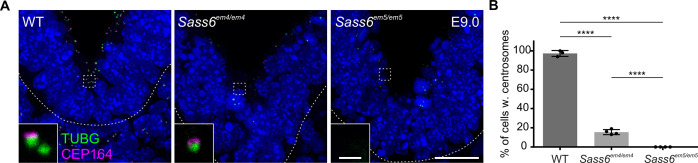
Figure 2. Sass6em4/em4 are severe hypomorphs while Sass6em5/em5 embryos lack centrioles.
(A) Left-side views of wild-type (WT), Sass6em4/em4, and Sass6em5/em5 embryos at E9.5. Anterior is up in all images. At least five embryos were analyzed per genotype. Scale bar = 500 µm. (B) Western blot analysis using a SAS-6-specific antibody on E9.5 WT, Sass6em4/em4, and Sass6 em5/em5 embryo extracts. Asterisks mark non-specific bands. GAPDH is used as a loading control. (C) Immunostaining for TUBG and SAS-6 on sagittal sections of WT, Sass6em4/em4, and Sass6em5/em5 embryos at E9.0. The sections shown encompass the neural plate (top) and mesenchyme (bottom), demarcated by the dashed line. Insets are magnifications of the center of the dashed squares. Dorsal is up in all images. Scale bars = 20 µm and 1 µm (insets). (D) Quantification of the percentage of cells with SAS-6 signal co-localization with TUBG in (C). Error bars represent mean ± SD WT: 95 ± 3% (n=1929 cells from three embryos); Sass6em4/em4: 19 ± 1% (n=542 from two embryos); Sass6em5/em5: 4 ± 2% (n=2458 from four embryos). ****p<0.0001, **p<0.01 (one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons). (E) Immunostaining for TUBG on transverse sections of Cetn2-eGFP, Sass6em4/em4 Cetn2-eGFP, and Sass6em5/em5 Cetn2-eGFP embryos at E9.0. The sections shown are similar to those described in (C). Insets are magnifications of the center of the dashed squares. Scale bars = 20 µm and 1 µm (insets). (F) Quantification of the percentage of cells with centrioles (TUBG and Centrin-eGFP) is shown in (E). Error bars represent mean ± SD Cetn2-eGFP: 98 ± 2% (n=11,196 cells from three embryos); Sass6em4/em4 Cetn2-eGFP: 6 ± 1% (n=9752 from four embryos); Sass6em5/em5 Cetn2-eGFP: 2 ± 0.5% (n=5559 from four embryos). ****p<0.0001, *p<0.05 (one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons). (G) Immunostaining for Ac-TUB on U-ExM sections from E9.0 embryos of the indicated genotypes. Scale bar = 200 nm. (H) Quantification of the percentage of mitotic spindle poles with centrioles in (G). Error bars represent mean ± SD WT: 100 ± 0% (n=65 spindle poles from three embryos); Sass6em4/em4: 11 ± 0.03% (n=62 from two embryos); Sass6em5/em5: 0 ± 0% (n=45 from three embryos). ****p<0.0001, **p<0.01 (one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons).