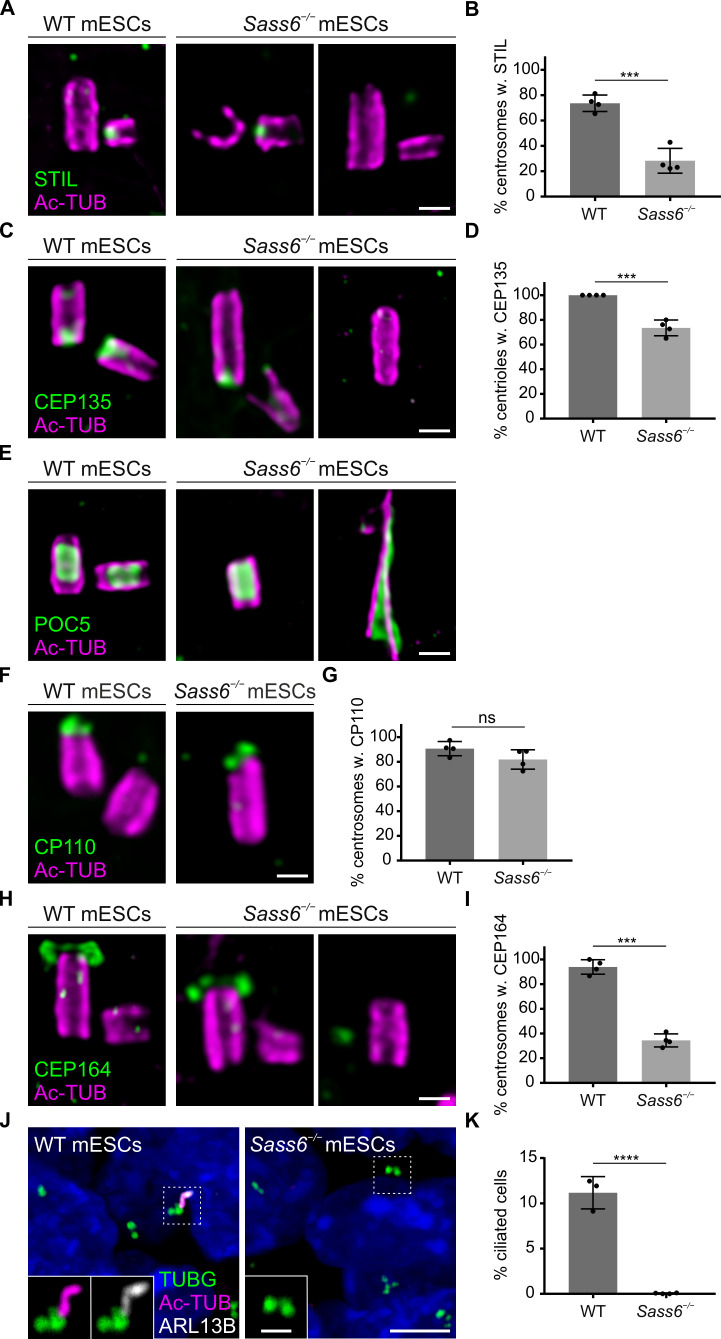
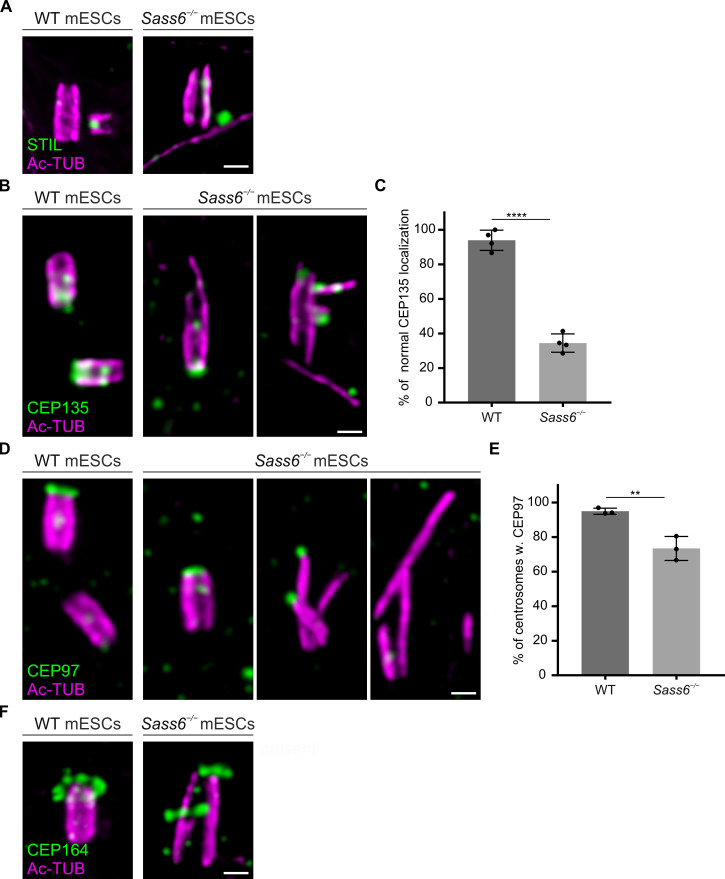
Figure 4. Centrioles in Sass6−/− mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) exhibit proximal and distal defects.
(A) Immunostaining for Ac-TUB and STIL of U-ExM of centrioles from wild-type (WT) and Sass6−/− mESCs. Examples of centrioles with or without STIL are shown. Scale bar = 200 nm. (B) Quantification of the percentage of centrosomes with (w.) STIL in (A) from four independent experiments. Error bars represent mean ± SD WT: 74 ± 6% (n=72 centrosomes); Sass6−/−: 29 ± 8% (n=94). ***p<0.001, (two-tailed Student’s t-test). (C) Immunostaining for Ac-TUB and cartwheel protein (CEP135) of U-ExM of centrioles from WT and Sass6−/− mESCs. Examples of centrioles with or without CEP135 are shown. Scale bar = 200 nm. (D) Quantifications of the percentage of centrioles with CEP135 in (C) from four independent experiments. Error bars represent mean ± SD WT: 100 ± 0% (n=160 centrioles); Sass6−/−: 73 ± 6% (n=98). ***p<0.001, (two-tailed Student’s t-test). (E) Immunostaining for Ac-TUB and the inner scaffold protein POC5 of U-ExM of centrioles from WT and Sass6−/− mESCs. Examples of normal-like or abnormal centrioles with POC5 are shown. Scale bar = 200 nm. (F) Immunostaining for Ac-TUB and the distal-end capping protein CP110 of U-ExM of centrioles from WT and Sass6−/− mESCs. Scale bar = 200 nm. (G) Quantification of the percentage of centrosomes with CP110 in (F) from four independent experiments. Error bars represent mean ± SD WT: 91 ± 5% (n=116 centrosomes); Sass6−/−: 82 ± 7% (n=106). ns = not significant with p>0.05 (two-tailed Student’s t-test). (H) Immunostaining for Ac-TUB and CEP164 of U-ExM of centrioles from WT and Sass6−/− mESCs. Examples of centrioles with or without CEP164 are shown. Scale bar = 200 nm. (I) Quantification of the percentage of centrosomes with mother centrioles (Ac-TUB) with the distal appendage marker (CEP164) in (H). Error bars represent mean ± SD WT: 94 ± 5% (n=104 centrosomes from four independent experiments); Sass6−/−: 28 ± 14% (n=140 from five experiments). ***p<0.001 (two-tailed Student’s t-test). (J) Immunostaining of the cilia markers ARL13B and Ac-TUB, and basal bodies marked with TUBG, on WT and Sass6−/− mESCs. The insets show separate channels for the magnifications of the center of the dashed squares. Scale bars = 5 µm and 1 µm (insets). (K) Quantification of the percentage of ciliated cells in (J). Error bars represent mean ± SD WT: 11 ± 1% (n=2602 cells from three experiments); Sass6−/−: 0 ± 0% (n=4602 from four experiments). ****p<0.0001 (two-tailed Student’s t-test).