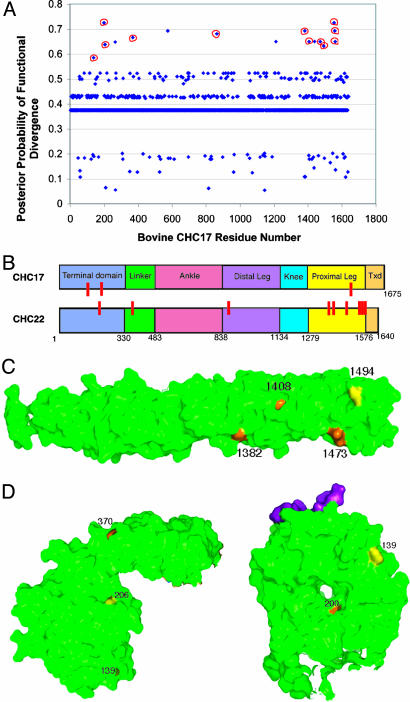
Fig. 4.
Site-specific profile for CHC evolutionary rate changes. The posterior probability of functional divergence [P(S1|X)] was quantitated by using diverge at each amino acid site in an alignment of CHC protein sequences. (A) Posterior probabilities of functional divergence at each sequence position of CHC17 and CHC22. Sixteen residues had posterior probabilities >0.58, which was calculated to indicate significant divergence. The 12 residues circled in red (139, 200, 206, 370, 864, 1382, 1408, 1473, 1494, 1555, 1559, and 1561) are depicted in B, C, and D below. diverge parameters for CHC22/CHC17 are ThetaML = 0.384, AlphaML = 0.283, SE Theta = 0.092, LRT Theta = 17.41. (B) CHC domains are represented on this bar diagram, with the location of residues with significant posterior probabilities of divergence noted in red on the isoform where it is more conserved. The approximate boundaries of each domain are numbered according to residue position in CHC17. Txd, trimerization domain. (C) Residues with predicted functional divergence between CHC17 and CHC22 are mapped onto the crystallographic structure (green) of the CHC proximal leg (27). Residues conserved only in CHC17 are noted in yellow, and those conserved only in CHC22 are noted in orange. (D) Residues with predicted functional divergence between CHC17 and CHC22 are mapped onto the crystallographic structure (green) of the terminal domain with the “clathrin box” peptide bound in its groove noted in purple (31). Residues conserved only in CHC17 are noted in yellow, and those conserved only in CHC22 are noted in orange.