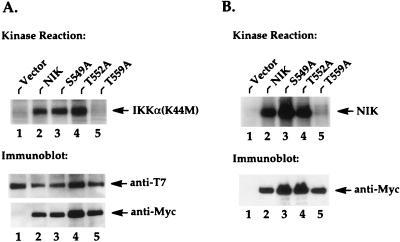
FIG. 3.
The NIK-T559A mutant protein fails to phosphorylate IKKα and to undergo autophosphorylation. (A) 293 cells were seeded at 5 × 105/well in six-well plates and transfected 24 h later with 2 μg of T7-tagged IKKα(K44M) expression vectors and 2 μg of Myc-tagged NIK expression vectors or vectors encoding the indicated mutant proteins. Twenty hours after transfection, in vitro kinase reactions were performed on anti-T7 immunoprecipitates from these cell lysates. The resulting kinase reactions were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose membranes, and analyzed by autoradiography. Phosphorylated IKKα(K44M) is indicated on the right in the upper part of the panel. The lower parts of the panel show the levels of immunoprecipitated IKKα and the levels of coimmunoprecipitated NIK proteins. (B) Two micrograms of Myc-tagged NIK expression vectors or the indicated mutants was transfected into 293 cells, and in vitro kinase reactions were performed on anti-Myc immunoprecipitates as described for panel A. Autophosphorylated NIK proteins are indicated on the right. The lower parts of the panel show the levels of immunoprecipitated NIK proteins present in the kinase reactions.