Figure 1.
Identification of ZmK2.1, a Maize Inward K+ Channel of the Shaker Family.
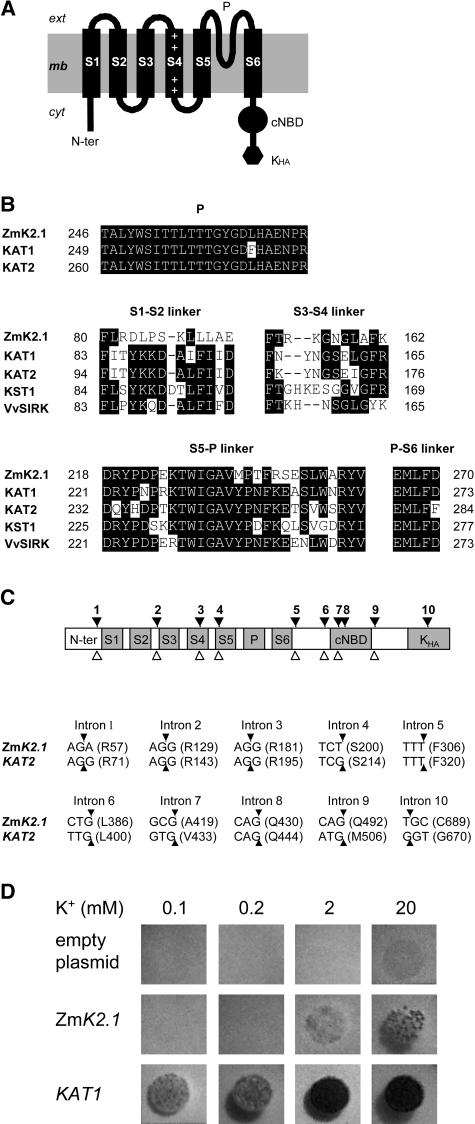
(A) Topology of the ZmK2.1 polypeptide. The hydrophobic core of Shaker channels typically displays six transmembrane segments, S1 to S6. S4, the channel voltage sensor, carries positively charged residues (+). The pore-forming domain (P) is present between S5 and S6. A putative cyclic nucleotide binding domain (cNBD) and a domain rich in hydrophobic and acidic residues (Kha) are present in the cytoplasmic C-terminal region.
(B) Comparison of the ZmK2.1 amino acid sequence with that of group 2 Shakers from other plant species (KAT1 and KAT2 from Arabidopsis, KST1 from potato, and VvSIRK from grapevine). Top, Alignment of the pore domains. Middle and bottom, Alignment of the S1-S2, S3-S4, S5-P, and P-S6 extracellular linkers.
(C) Structure of ZmK2.1. Top, The positions of the 10 introns identified in the ZmK2.1 gene, indicated by black arrowheads, strictly correspond to those of the 10 introns identified in the Arabidopsis KAT2 Shaker channel gene. The open arrowheads below indicate the positions of the eight introns in the Arabidopsis KAT1 Shaker gene. Bottom, Conservation of intron positions within the coding sequence between ZmK2.1 and KAT2. For each intron, the interrupted codon, if any (the arrowheads indicate the positions of the interrupting introns), or the codon just upstream of the intron is given. The corresponding amino acid (single-letter code) and the position of this residue in the predicted sequence are indicated in parentheses.
(D) Yeast complementation tests. The yeast Wagf2 strain deficient for K+ uptake was transformed with either the empty pFL61 plasmid (control), ZmK2.1 cDNA in pFL61, or the Arabidopsis KAT1 cDNA in pFL61. Drop tests were performed on selective agar media containing 0.1, 0.2, 2, or 20 mM K+ (added as KCl). The plates were photographed after 3 d of incubation at 28°C.