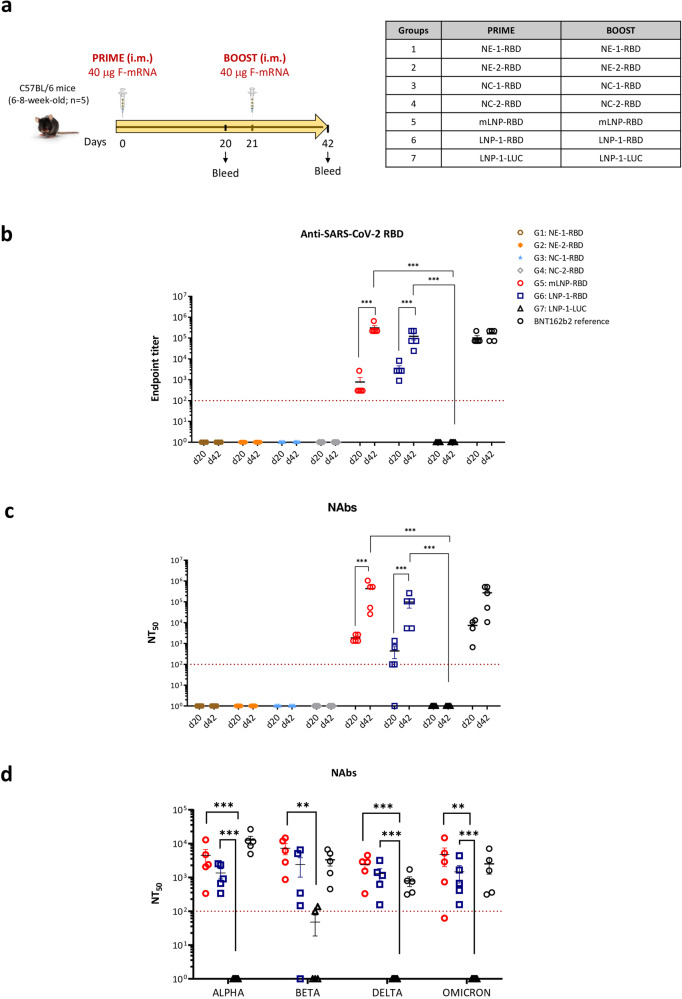
Fig. 2. Humoral immune responses induced in C57BL/6 mice by different nanocarriers containing RBD-mRNA.
a Immunization schedule. Female C57BL/6 mice (n = 5) were immunized with two doses of 40 µg of the different formulations containing RBD-mRNA by intramuscular (i.m.) route as indicated. b SARS-CoV-2 RBD-specific IgG binding antibodies. Anti-RBD IgG titers were determined in individual sera obtained at 20 days post-prime (d20) or 21 days post-boost (d42) by ELISA. An unpaired nonparametric Mann–Whitney test of transformed data was used. ***p < 0.001. c SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody responses. NT50 titers were determined in individual sera harvested at d20 and d42 using a live virus microneutralization assay (MAD6 strain, containing D614G mutation). An ordinary one-way ANOVA of transformed data followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test was performed. ***p < 0.001. d Neutralizing antibody responses induced against SARS-CoV-2 variants. NT50 titers were evaluated in individual serum samples harvested at d42 by a live virus microneutralization assay using the SARS-CoV-2 Alpha (B.1.1.7), Beta (B.1.351), Delta (B.1.617.2) and Omicron (B.1.1.529) variants. An ordinary one-way ANOVA of transformed data followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test was performed. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. Serum samples from mice similarly vaccinated with two doses of 5 μg of BNT162b2 vaccine (mRNA vaccine from Pfizer-BioNTech) were used as a reference value (BNT162b2 reference). Red dashed line represents the lower limit of detection of the assay. Mean with standard error of the mean (SEM) is represented.