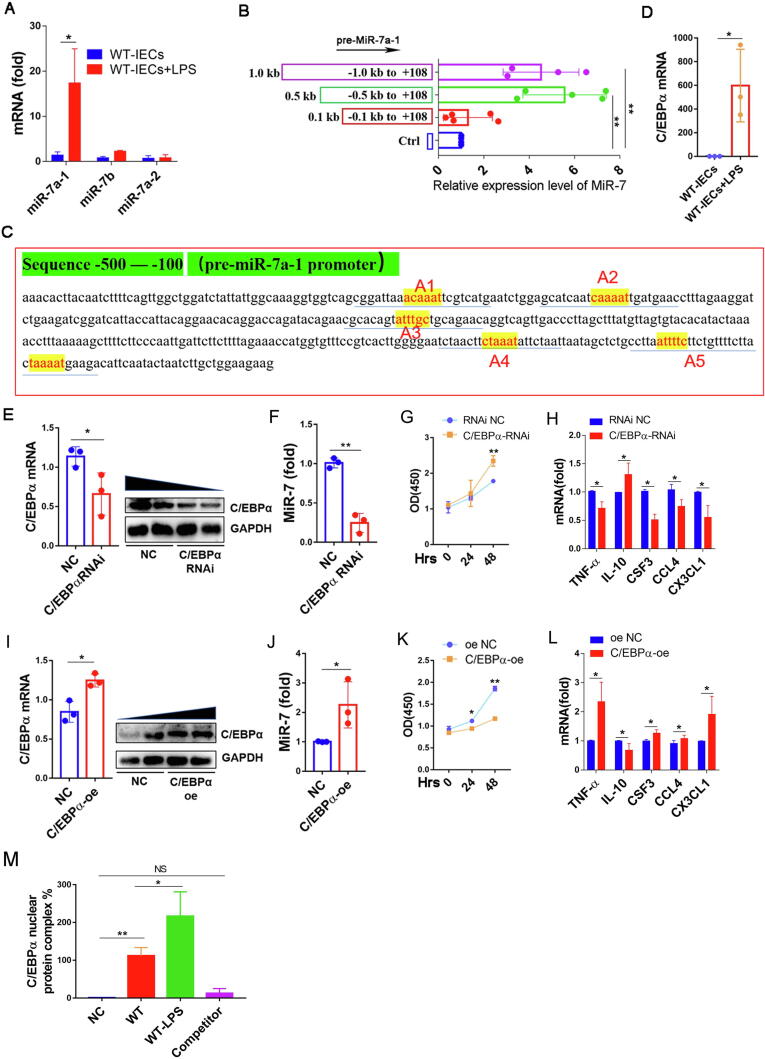
Fig. 4.
C/EBPα is an upstream regulator of murine miR-7 expression in IECs. (A) WT-IECs were isolated, cultured and stimulated with LPS (500 ng/ml) or a control. 24 h later, Real-time PCR analysis for pri-miR-7a-1, pri-miR-7a-2, and pri-miR-7b; (B) WT-IECs transferred with different plasmids (p-1000-miR-7, p-500-miR-7, or p-100-miR-7) were cultured as described previously. 48 h later, Real-time PCR analysis for mature miR-7. (C) Biological analysis showed the potential binding sites (from − 500 to − 100 site) for transcription factor C/EBPα in the miR-7a-1 promoter sequence (yellow A1-A5). (D) WT-IECs were stimulated with LPS or a control. 24 h later, Real-time PCR analysis for C/EBPα; (E-F, I-J) WT-IECs were infected with C/EBPα RNAi and RNAi-NC or C/EBPα overexpression and oe-NC virus particle, 48 h later, Immunoblot and Real-time PCR analysis of C/EBPα, and Real-time PCR analysis for miR-7; the cell proliferation capacity was observed at the indicated time points by CCK8 (G, K). Real-time PCR analysis for inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-10, CSF4, CCL4 and CX3CL1 (H, L). (M) EMSA analysis showed the ability of C/EBPα binding to the core promoter sequence (A5) of the miR-7a-1 gene. The values are the means ± SD (n = 3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, NS no significant. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)