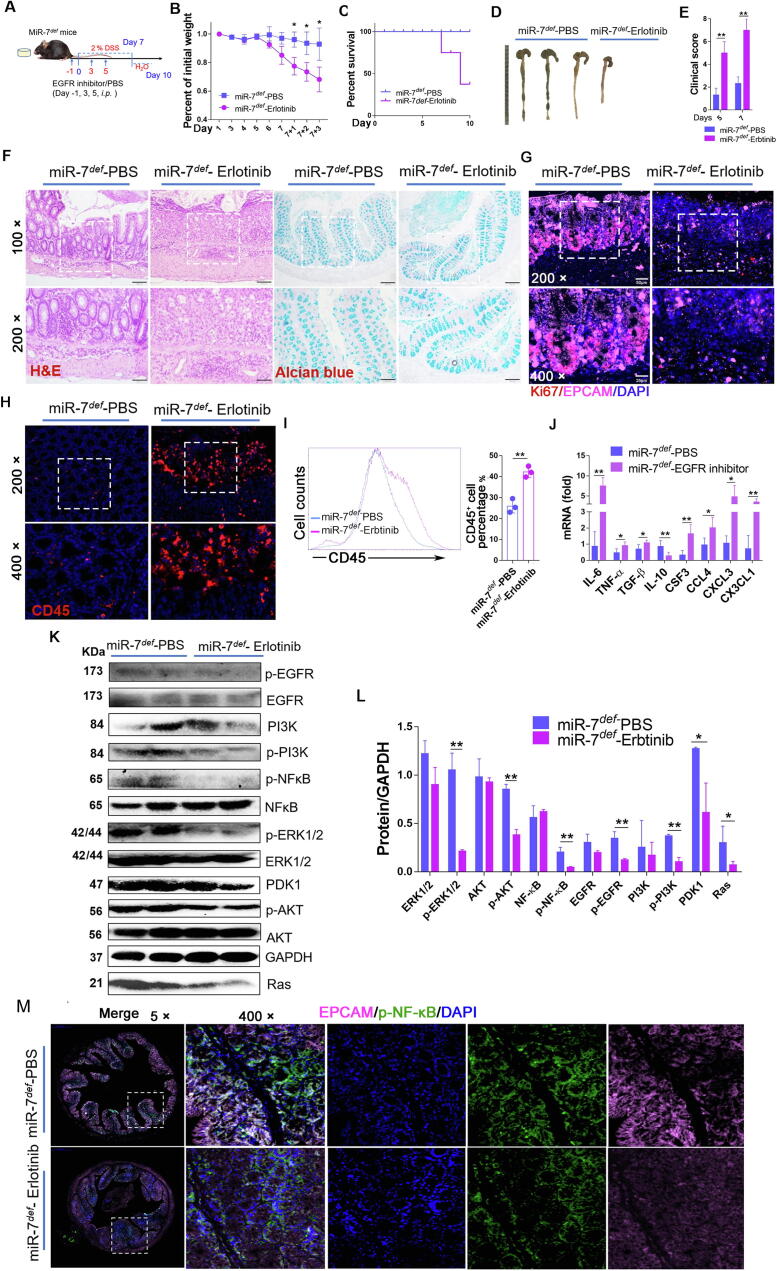
Fig. 6.
Downregulated EGFR signaling aggravates the pathology of the miR-7def IBD model. (A) Schematic representation of the in vivo experiment. MiR-7def mice (8–10 W, n = 6) were injected intraperitoneally with Erlotinib (50 mg/kg) on DSS for −1, 3 and 5 days, and the IBD model was established as described previously (The mice were injected intraperitoneally with cosolvent PBS for contrast); The body weight loss (B), the survival curve (C), representative gross images of colon (D), and the clinical scores (E) were analyzed; Histopathology was performed by H&E staining and mucin production detected by Alcian blue staining (×100, ×200) (F); The expression of Ki67 and EPCAM (G) or CD45 (H) were detected by IF (×200, ×400); FCM analysis of CD45+ cells in colon (I); Real-time PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines IL-6, TNF-α, TGF-β, IL-10, CSF4, CCL4, CXCL3 and CX3CL1 in the colon (J); Immunoblot analysis of p-EGFR, EGFR, PI3K, p-PI3K, NF-kB, p-NF-kB, AKT, p-AKT, ERK, p-ERK, Ras and PDK1 in colorectal tissues (K–L); The expression of p-NF-kB and EPCAM were determined by multiplexed fluorescent immunohistochemical staining in colon (×5, ×400). The values are the means ± SD (n = 6). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)