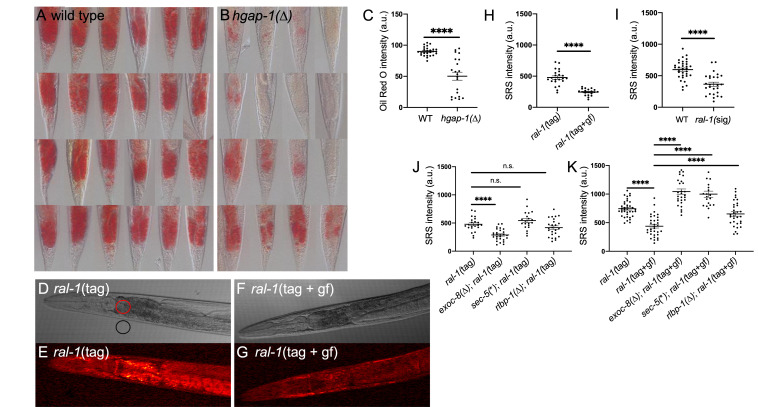
Figure 1. RAL-1 regulates lipid homeostasis, biosynthesis and/or storage .
A-C) Using an Oil Red O staining protocol we found that lipid storage was decreased in B) hgap-1 ( ∆ ) relative to (A) wild-type animals. These data are quantitated in (C) as arbitrary units (a.u.) (P < 0.0001; posterior intestine showed). D-H ) Stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS) imaging of lipid levels revealed decreased lipid in animals with constitutively active RAL-1 . DIC ( D, F ) and SRS ( E,G ) imaging of animals with RAL-1 tagged at the N-terminal with mKate2::3xFlag. Wild-type ( D, E ) were compared to G26V constitutively activated RAL-1 ( F, G ). Pixel intensity was measured from the SRS images ( E, G ) in the areas illustrated with red and black circles of 35 μm ( D ). Background (black circle) was subtracted from the anterior intestine (red circle) in the SRS image to yield a value for lipid content. These data for various experiments were graphed as normalized SRS intensity ( H-K ). H ) Comparison of tagged wild-type vs. G26V constitutively activated RAL-1 animals. I ) Comparison of wild-type vs. ral-1 ( sig ) ( ral-1 ( gk628801 [R139H]) signaling deficient RAL-1 (no tag for either). J ) Comparison of tagged RAL-1 single mutant or double mutants with mutations in exoc-8 , sec-5 , or rlbp-1 . exoc-8 ( Δ ) is the ok2523 deletion, rlbp-1 ( Δ ) is the tm3665 deletion, and sec-5 ( * ) causes a premature stop at codon 369 of 884 residues in SEC-5. K ) Comparison of tagged wild-type or G26V constitutively active RAL-1 single mutant or double mutants with mutations in exoc-8 , sec-5 , or rlbp-1 . Data within each panel were scored concurrently but data between panel scored on different days. (Note difference in baseline of tagged RAL-1 between panels J and K . Data in C , H , I , J and K were subjected to the T-test.) Error bars represent SEM. *<0.05, **<0.01, ***<0.001, ****<0.0001, n.s. = not significant.