Fig. 5.
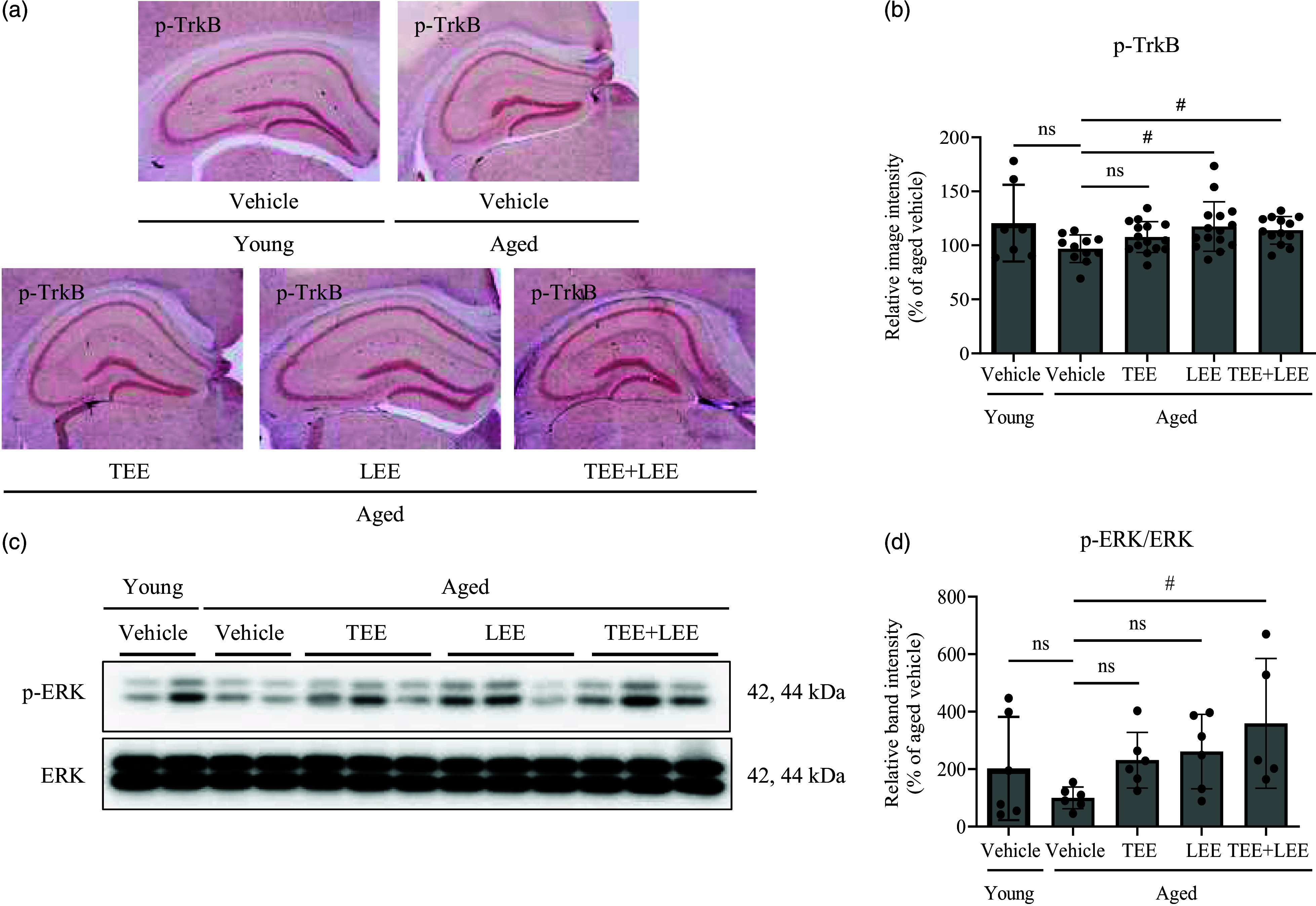
Tomato (TEE) and lemon ethanolic extract (LEE) increased tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) phosphorylation in the hippocampus of aged mice. Oral administration of TEE and LEE activated the TrkB/ERK signalling pathway in the hippocampus of aged mice. Phosphorylation of BDNF receptor was quantified by p-TrkB immunostaining. (a) Representative images of TrkB+ cells in the hippocampal region. Arrows indicate TrkB+ cells, and (b) the total number of TrkB+ cells in the DG is quantified in the graph. (young + vehicle, n 5 mice; aged + vehicle, n 4 mice; aged + TEE, n 4 mice; aged + LEE, n 5 mice; aged + TEE and LEE, n 5). Each bar represents the mean ± se for each group. (c) Changes in the expression of phosphorylated ERK in the mouse hippocampus were analysed by western blotting. (d) The bands shown are the four representative bands from each group. The relative protein expression of phospho-ERK was analysed using ImageJ software. The intensity of the bands was normalised to that of total ERK. (young + vehicle, n 6 mice; aged + vehicle, n 6 mice; aged + TEE, n 6 mice; aged + LEE, n 6 mice; aged + TEE and LEE, n 5). Each bar represents the mean ± se for each group. Statistical significance was determined by Kruskal–Wallis H test followed by post hoc Dunn’s test. # P < 0·05 v. aged vehicle group.
