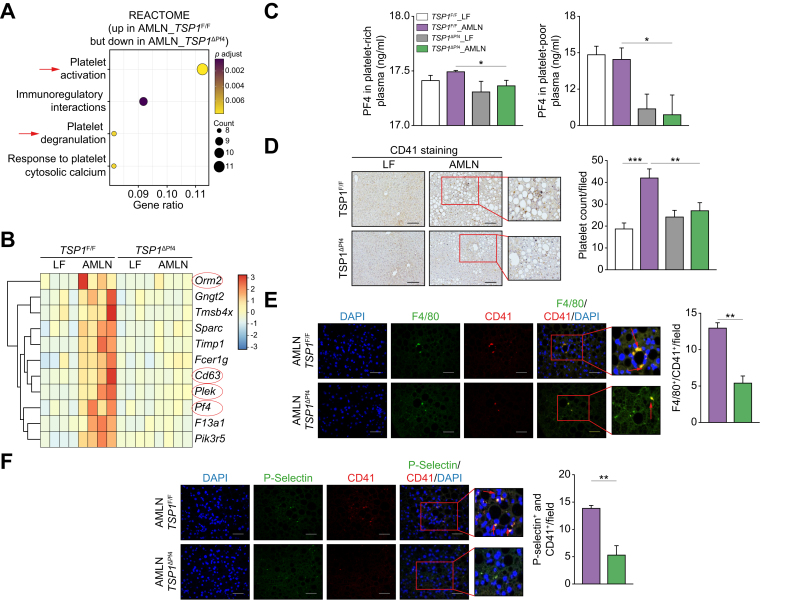
Fig. 7.
Deletion of TSP1 in platelets reduced intrahepatic platelet accumulation and activation in 32-week AMLN diet-fed mice.
(A) Reactome pathway analysis of liver transcriptome data from Fig. 5A; (B) Hierarchical clustering analysis of genes in platelet activation, signaling and aggregation category from Reactome pathway. The color spectrum from blue to red represents the gene expression intensity from low to high, respectively; (C) CXCL4/PF4 levels from both platelet-rich plasma and platelet-poor plasma was measured; (D) Representative image of CD41 immunohistochemistry staining in liver sections (scale bar = 100 μm) and semi-quantification data; (E) Representative immunofluorescence image of F4/80 and CD41 co-staining in liver sections (scale bar = 100 μm). Nuclei were stained with DAPI; (F) Representative immunofluorescence image of P-Selectin and CD41 co-staining in liver sections and semi-quantification data, Scale bar = 100 μm. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Data are represented as mean ± SE (n = 5 mice/group); one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. ∗p <0.05, ∗∗p <0.01, ∗∗∗p <0.0001. LF, low fat.