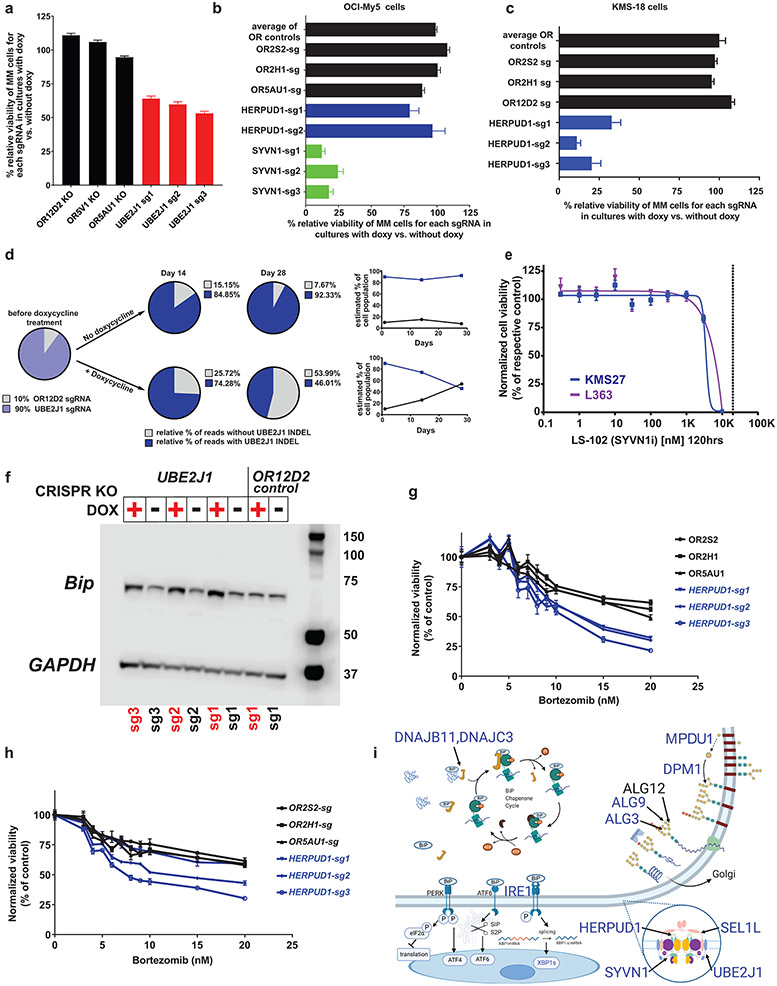
Figure 7: ∣. Biological role of UBE2J1 and other ER-associated MM-preferential dependencies.
a–d, Doxy-inducible CRISPR KO of ER-associated MM preferential dependencies or control OR genes in KMS-18 (a, c and d) or OCI-My5 (b) MM cells. Cells were cultured with or without Doxy (14 days in a–c; 14 or 28 days in d). In a–c, cell viability was evaluated by CTG (mean ± SEM), one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post-hoc tests (see source data) at P < 0.001 for each ER gene sgRNA (except HERPUD1 in b) vs. each of the OR sgRNAs; 80, 32 and 40 independent replicate cell cultures/sgRNA in a–c, respectively. In d, KMS18 cells with Doxy-inducible SpCas9 and transduced with sgRNA against UBE2J1 or OR2D12 were mixed at a 9:1 ratio, respectively, in a competition assay. INDEL analyses (at days 14 and 28) calculated the relative percentage of cells with CRISPR-induced frameshift mutations of UBE2J1. e, In vitro treatment with SYVN1 inhibitor LS-102 (5 days; vertical dotted line represents reported in vitro half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) for inhibition of this target). CTG; mean; biological replicates N = 30 independent replicate cell cultures for drug-free controls in both lines, n = 3 or 4 independent replicate cell cultures, respectively, in L363 and KMS27 MM cells for each drug dose; nonlinear curve fitting with variable slope (four parameters). f, Immunobloting for BiP, a marker of ER stress, in KMS18 cells with Doxy-inducible CRISPR KO of UBE2J1 or control OR gene, cultured with versus without Doxy. g,h, In vitro bortezomib treatment (24 h) of KMS18 (g) or OPM-2 (h) cells with Doxy-inducible CRISPR KO of HERPUD1 or control OR genes. (CTG; mean ± SEM; n = 8 independent replicate cell cultures for drug-free controls and n = 4 independent replicate cell cultures per drug dose for each KO; two-way ANOVA (P < 0.001); detailed results of Tukey posthoc tests in source data). i, Schematic figure of ER-associated dependencies. MM-preferential ER dependencies (blue symbols) involve ER membrane protein complexes mediating dislocation of misfolded ER proteins to cytosol (e.g. HERPUD1, SEL1L) and associated ER-specific E2/E3 enzymes (SYVN1, UBE2J1, UBE2G2); enzymes (e.g. DPM1, ALG3, ALG9) required for N-glycan-dependent surveillance of quality control for luminal ER glycoproteins; chaperones (e.g. DNAJB11, DNAJBC3) for BiP complexes with misfolded proteins; and the known ER stress-sensor IRE1a (ERN1) and its downstream transcription factor XBP1.