Extended Data Fig. 11 |. DNA-PK interacts with structured RNAs that can activate its kinase.
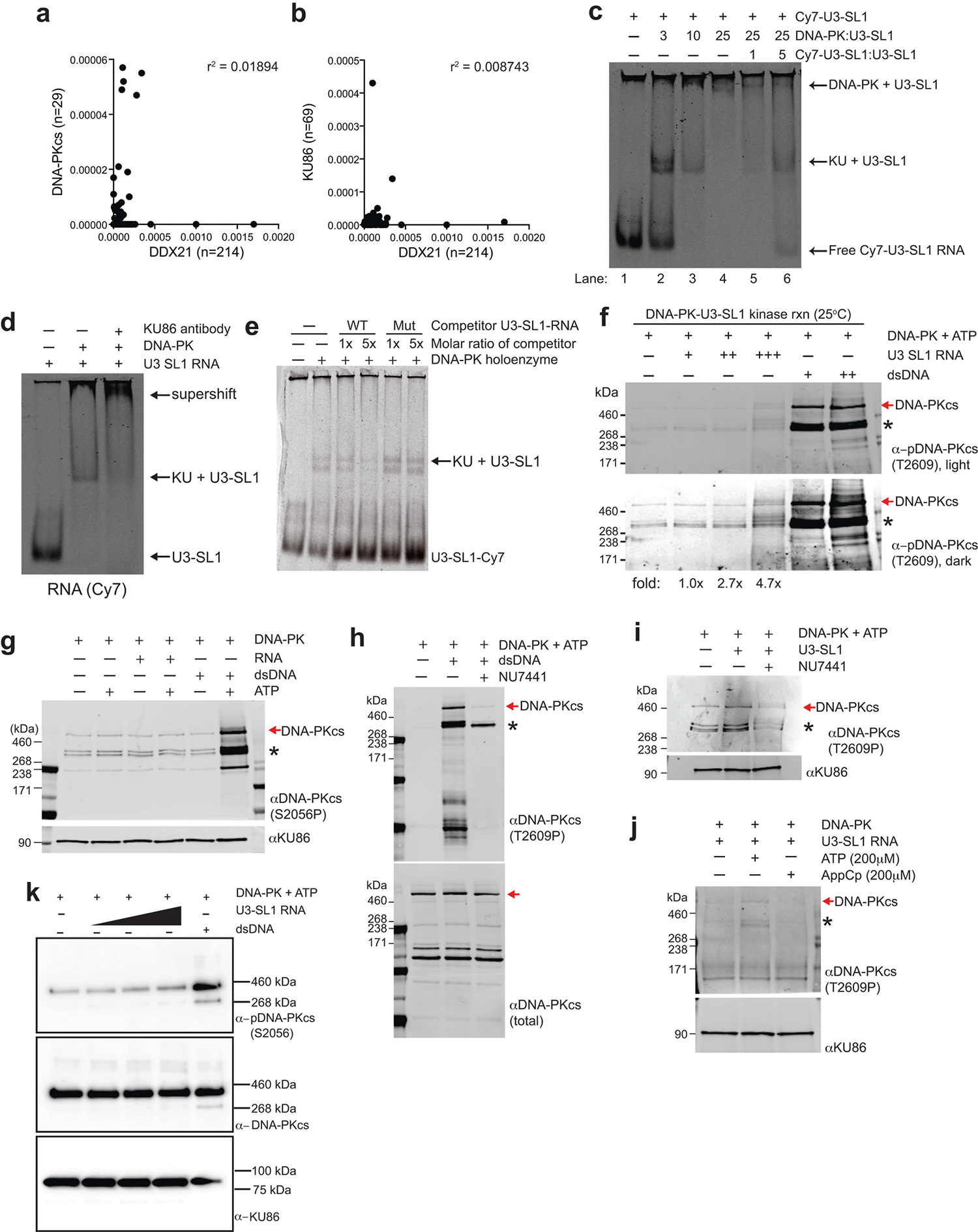
a, b, Correlation analysis of total RT stops mapping to non-repeat snoRNA transcripts from DDX2135 compared to DNA-PKcs (a) or KU86 (b) irCLIP experiments from DMSO-treated HeLa cells. Correlation analysis was performed using Pearson’s correlation coefficient. n denotes number of snoRNA transcripts bound by each protein. c, EMSA of purified human DNA-PK and in vitro transcribed U3-SL1. Lane 1 contains only Cy7-labelled U3-SL1. Lanes 2–4 show that KU assembles with U3-SL1 at a 1:3 molar ratio, while DNA-PK holoenzyme assembly occurs at a 1:25 molar ratio. Lanes 5 and 6 show that unlabelled U3-SL1 RNA competes away bound labelled U3-SL1 in a dose-dependent manner. d, Supershift EMSA of DNA-PK and U3-SL1 RNA with KU86 antibody. The addition of anti-KU86 confirms the identity of the KU–U3-SL1 band and also shifts up the complex to higher molecular weights. e, A structural mutant of U3-SL1 was generated by introducing point mutations predicted to disrupt the stem-loop structure. This mutant was unable to compete away wildtype U3-SL1 for binding to the KU complex, while unlabelled wild-type U3-SL1 competed efficiently. f, DNA-PK in vitro kinase phosphorylation assay in the presence of increasing amounts of U3-SL1 or DNA. Western blot was performed with an antibody recognizing DNA-PKcs phosphorylated at the T2609 cluster. Asterisks denote cross-reactive fragments that probably include phosphorylated DNA-PKcs fragments, on the basis of MS analyses of the DNA-PK complex (Extended Data Fig. 9c, d). g, As in f, but using an antibody recognizing DNA-PKcs phosphorylated at the S2056 cluster. h–j, As in f with the following changes. h, dsDNA was used to activate DNA-PK, NU7441 was included to inhibit specific DNA-PK activity, and western blot analysis monitored the total DNA-PK (total DNA-PKcs) or phosphorylated DNA-PK (DNA-PKcs phoT2609). i, U3-SL1 RNA was used to activate DNA-PK in the absence or presence of the DNA-PK inhibitor NU7441. j, U3-SL1 RNA was used to activate DNA-PK, hydrolysable (ATP) or non-hydrolysable (AppCp) ATP was provided, and western blot analysis monitored KU86 (loading control) or phosphorylated DNA-PK (phoT2609). k, Baculovirus-purified human DNA-PK in vitro kinase phosphorylation assay in the presence of increasing amounts of U3-SL1 or DNA. Western blot was performed with antibodies recognizing DNA-PKcs phosphorylated at the S2056 cluster (top), total DNA-PK (middle) and KU86 (bottom). All EMSA and western blots presented here are representative of three biologically independent experiments.
