Figure 3:
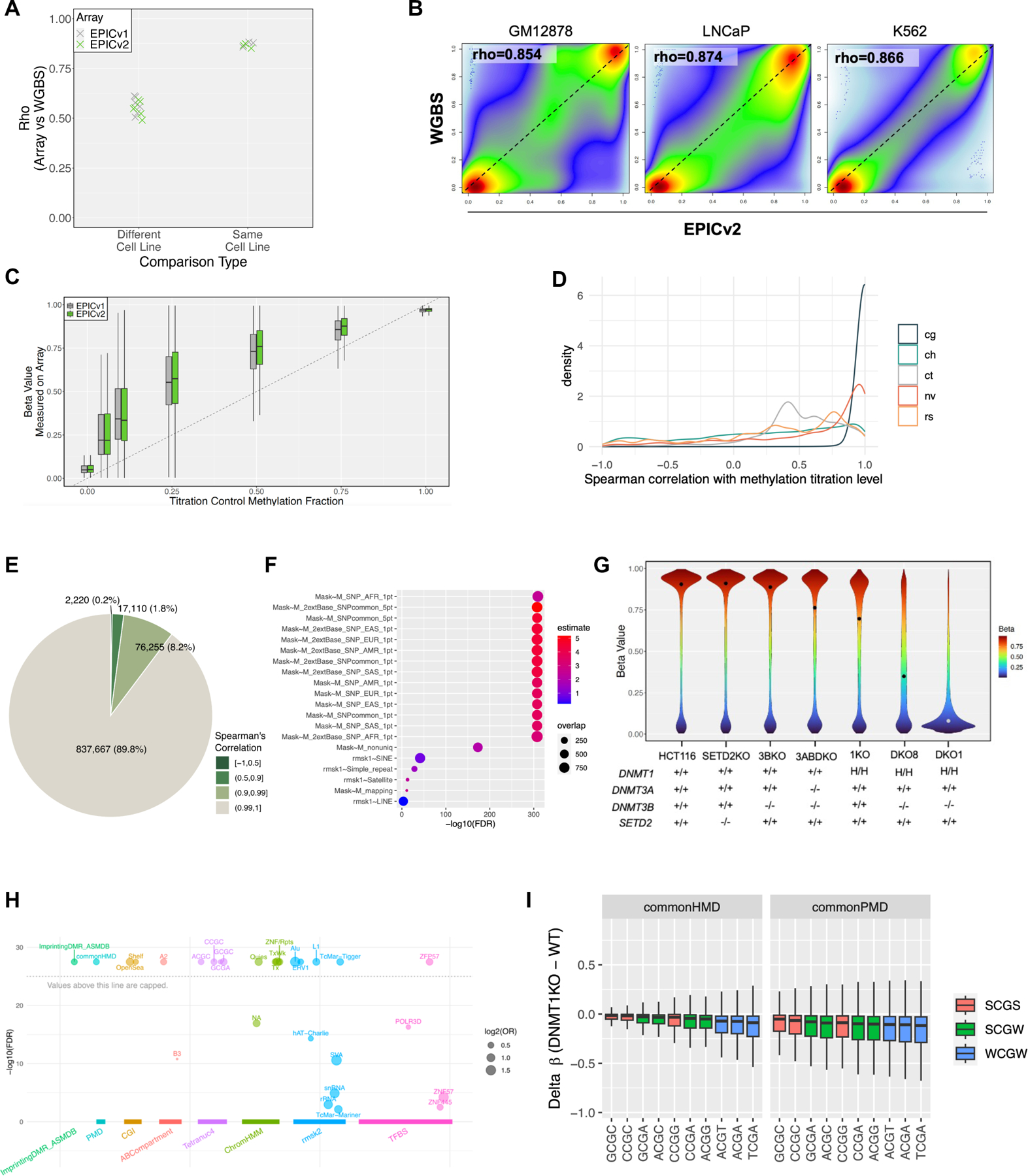
EPICv2 reveals DNA methylation variation in wild type cell lines and cell line models of epigenetic modifiers. (A) EPICv2-WGBS correlation between the same and different cell lines. (B) Comparison of EPICv2-measured DNA methylation level with whole genome bisulfite sequencing (WGBS) on GM12878, LNCaP and K562. (C) Comparison of EPICv2 accuracy on cell line DNA of known titrated methylation fractions. (D) Correlation of EPICv2 probes with known DNA methylation level in titration experiment. (E) Distribution of probes by correlation with titrated fraction. (F) Functional analysis of poorly correlated probes. (G) Drop of global DNA methylation levels in HCT116-derived cell lines with mutated or deleted DNMTs and/or SETD2. (H) Enrichment of CpGs that retain DNA methylation in DKO1 cells. (I) Sequence context of loss of DNA methylation in DNMT1KO cells, stratified by common partially methylated domains (PMDs) vs. common highly methylated domains (HMDs), and CpGs flanked by A/T (W) or G/C (S).
