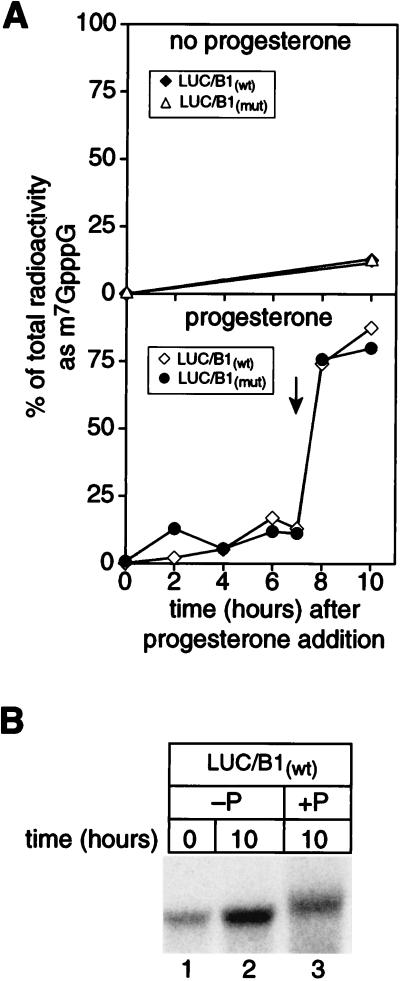
FIG. 3.
N-7 methylation of the cap is independent of polyadenylation and occurs at nuclear breakdown. (A) Cap methylation of mRNAs occurs near the time of nuclear breakdown and is independent of polyadenylation. Cap radiolabeled luciferase-cyclin B1 mRNAs with and without a point mutation in AAUAAA (LUC/B1mut and LUC/B1wt, respectively) were prepared as described in the text. RNAs were injected into oocytes, and progesterone was added. Samples of five oocytes were taken at intervals thereafter, and histone H1 kinase activity was determined for half of each sample. RNA was extracted from the remaining sample and analyzed by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (see below), as well as nuclease P1 digestion and 2D TLC. The y axis shows the percentage of total radioactivity in each sample present as m7G*pppG and is plotted against the time after progesterone addition. The time at which histone H1 kinase activity first increased (indicated by an arrow) was concurrent with the onset of nuclear breakdown (approximately 7.5 h). ⧫, LUC/B1wt mRNA, no progesterone; ▵, LUC/B1mut mRNA, no progesterone; ◊, LUC/B1wt mRNA, progesterone added; •, LUC/B1mut mRNA, progesterone added. (B) Polyadenylation of LUC/ B1wt mRNA. The remaining portion of extracted mRNA was analyzed by denaturing gel electrophoresis. Samples were taken immediately following microinjection (lane 1) or after 10 h in the absence (−P; lane 2) or presence (+P; lane 3) of progesterone.