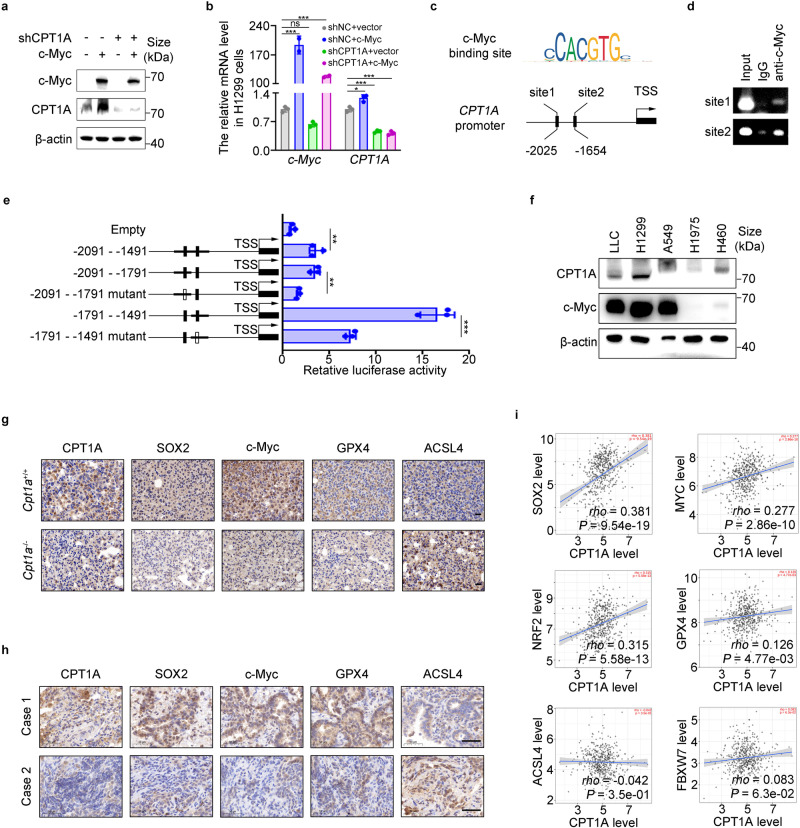
Fig. 5.
c-Myc transcriptionally activates CPT1A to form a mutually reinforcing intermolecular loop in lung cancer cells. Analysis of CPT1A expression in H1299-shNC/shCPT1A cells transfected with c-Myc or control plasmid. Quantification of mRNA (a) and representative western blot for c-Myc and CPT1A (b). Data represent the mean ± s.d.; n = 3 samples. c The DNA sequence of c-Myc binding motif and the binding sites of c-Myc in the promotor of CPT1A gene predicted by PROMO website. d Chromatin immunoprecipitation with c-Myc antibody and RT-PCR for c-Myc binding sites. e A dual-luciferase reporter assay to investigate the transcriptional activity of the c-Myc binding sites in H1299 cells transfected with plasmids containing wild type or mutant binding site. Data represent the mean ± s.d.; n = 3 samples. f Representative western blot for CPT1A and c-Myc in distinct lung cancer cell lines. g Representative IHC staining for CPT1A, SOX2, c-Myc, GPX4 and ACSL4 in the tumor of Cpt1a+/+ or Cpt1a-/- transgenic mice. Scale bar: 20 μm (insets). h Representative IHC staining for CPT1A, SOX2, c-Myc, GPX4 and ACSL4 in the tumor of NSCLC patients. Scale bar: 50 μm (insets). i Correlation analysis between CPT1A and SOX2/c-Myc/NRF2/GPX4/ACSL4/FBXW7 transcripts by using TCGA dataset. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; ns: not significant. The statistical analysis was performed using a two-tailed Student’s t-test or Pearson’s correlation test or log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test