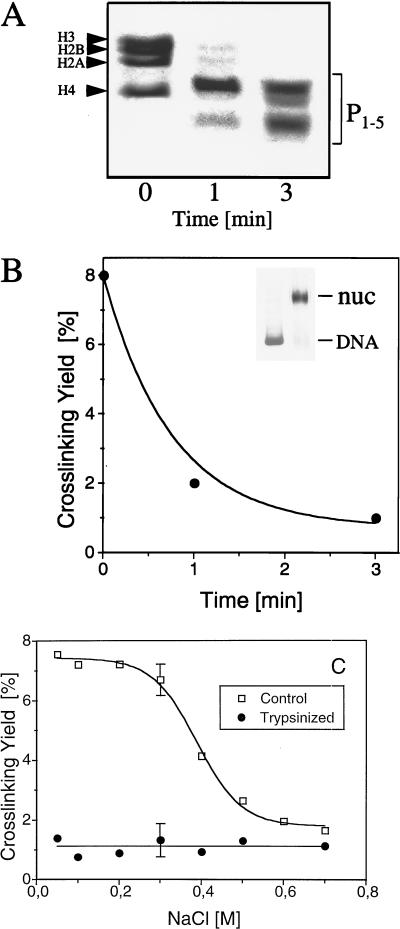
FIG. 2.
Core histones are cross-linked to DNA via their NH2 tails. (A) Electrophoresis (18% polyacrylamide–SDS) of histones isolated from donor nucleosomes digested with trypsin for the indicated times. P1–5, trypsin-resistant peptides of the core histones, designated as described by van Holde (67). (B) Dependence of the yield of cross-linked DNA on reconstituted nucleosomes containing trypsinized histones. Nucleosomes were reconstituted under optimal conditions (3 μg of donor nucleosomes for 30 ng of 32P-labeled 180-bp probe DNA) by using as donors either native nucleosomes or nucleosomes digested with trypsin for 1 or 3 min. Each sample was irradiated with a single 266-nm laser pulse at a laser intensity of 25 MW/cm2. The amount of cross-linked DNA was measured by the phenol extraction method, and the yield of cross-linked DNA was plotted against the time of trypsin digestion of donor nucleosomes. The inset represents the mobilities of the naked 180-bp DNA fragment and of reconsti- tuted particles (nuc) determined by using as donors nucleosomes digested with trypsin for 3 min. (C) NaCl concentration dependence of the yield of cross-linked DNA on nucleosome particles reconstituted with native histones or with histones from donor nucleosomes that had been digested with trypsin for 3 min. Both samples at different NaCl concentrations were irradiated with a single laser pulse (25 MW/cm2), and the dependence of the yield of cross-linked DNA (measured by phenol extraction) on NaCl concentration was determined. Each experimental point represents the average of four independent experiments. Because the errors of measurements at different ionic strengths were found to be essentially the same, for simplicity error bars are shown for only two experimental points.