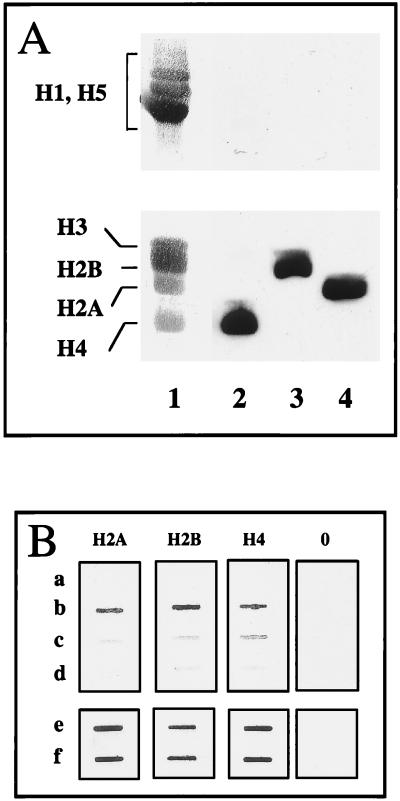
FIG. 3.
Immunochemical evidence for selective histone NH2 tail-DNA cross-linking induced by UV laser irradiation. (A) Specificity of the histone antibodies used. Hen erythrocyte histones were separated by 18% polyacrylamide–SDS gel electrophoresis, electroblotted, and stained with India ink (lane 1) or reacted with immunopurified antibodies against H4 (lane 2), H2B (lane 3), and H2A (lane 4). (B) Immunoslot assay for the presence of core histones in cross-linked protein-DNA complexes obtained upon irradiation of nucleosomes. Nucleosomes containing 180 bp of DNA were reconstituted by histone octamer transfer by using as donors either native nucleosomes or nucleosomes digested with trypsin for 1 or 3 min. The samples were irradiated with identical doses, and the cross-linked histone-DNA complexes were separated from the free histones on CsCl gradients. The CsCl gradients were fractionated, and the fractions containing the DNA peak were pooled. Five micrograms (measured as DNA) from each pooled sample was dotted on a nitrocellulose filter and reacted with antibodies against H2A, H2B, and H4 and preimmune IgG (0). a, Nonirradiated particles; b, irradiated particles; c and d, irradiated particles containing 1- and 3-min trypsin-digested histones, respectively; e and f, control slots showing the reaction of the antibodies with nucleosomes containing native or 3-min trypsin-digested histones.