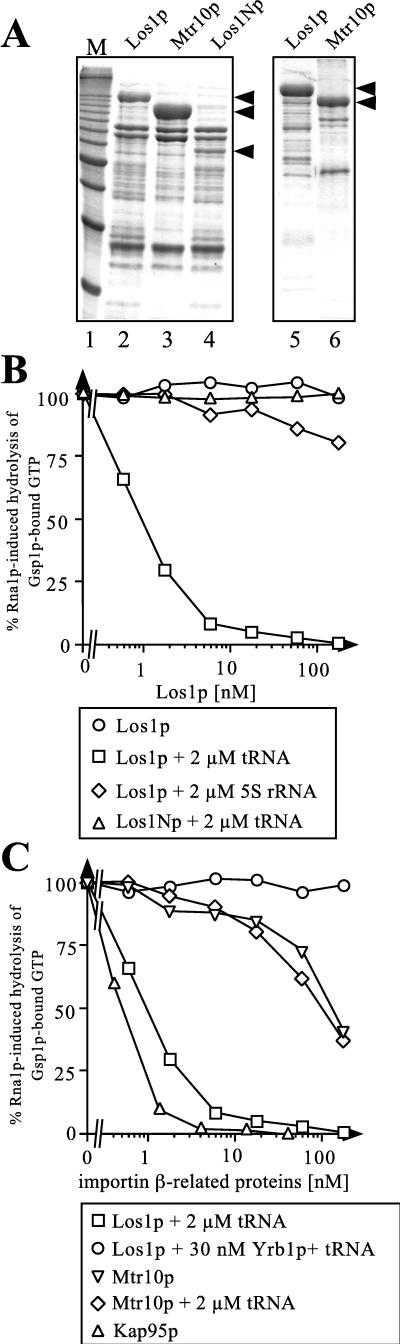
FIG. 6.
Interaction of recombinant Los1p with Gsp1p-GTP and tRNA. (A) His6-tagged Los1p-, Mtr10p-, and Los1Np-containing E. coli lysates were passed through a Ni-NTA–agarose column, and bound proteins were eluted with 200 mM imidazole, desalted, concentrated, and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining (lanes 2 to 4). In the case of Los1p and Mtr10p, Ni-NTA column eluates were subsequently passed through an ion-exchange column (Mono Q) and bound proteins were eluted with an NaCl gradient. The fractions containing Los1p or Mtr10p were pooled, desalted, concentrated, and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining (lanes 5 and 6). Minor bands in these preparations represented mostly degradation products. From top to bottom, arrowheads indicate the positions of Los1p, Mtr10p, and Los1Np, respectively. Lane 1 contains molecular mass standards (M; 10-kDa ladder; the most intense band corresponds to 50 kDa). (B and C) Cooperative binding of Gsp1p-GTP and tRNA to Los1p. Gsp1p-[γ-32P]GTP (50 pM) was preincubated for 15 min either with the importin-β-related proteins alone, with these proteins as mixtures with tRNA or 5S rRNA in the indicated concentrations, or with incubation buffer. Then 20 nM Rna1p was added, and the reaction was allowed to proceed for 2 min. Where indicated, Yrb1p was added immediately before the addition of Rna1p. Hydrolysis of Gsp1p-bound GTP was determined as released [32P]phosphate.