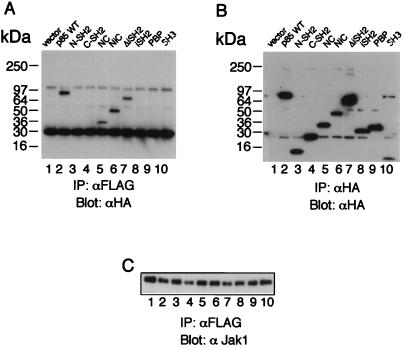
FIG. 5.
Both of the SH2 domains of p85 are required for its efficient association with Jak1. (A) 293 T+ cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged Jak1 and with the indicated HA-tagged forms of p85. Immunoprecipitations (IP) with anti-FLAG M2 MAb were followed by Western blotting with anti-HA MAb. The p85 constructs (described in reference 10) are as follows: N-SH2, residues 329 to 439, spanning the more N-terminal of the two SH2 domains in p85; C-SH2, residues 563 to 724, spanning the more C-terminal SH2 domain; NC, residues 329 to 439 plus residues 563 to 724, containing both SH2 domains but lacking the p110 binding (inter-SH2) region; NiC, residues 329 to 724, like NC except that it includes the inter-SH2 region; ΔiSH2, full-length p85 that lacks the 439–563 inter-SH2 region; iSH2, residues 425 to 616, a construct that contains only the inter-SH2 region; PBP, residues 79 to 328, containing the Pro-Bcr-Pro region located between the SH3 and N-terminal SH2 domains of p85; and SH3, residues 1 to 78, spanning the SH3 domain. All constructs have N-terminally positioned HA tags. WT, wild type. (B) Expression control for the HA-tagged forms of p85. (C) Expression controls for Jak1.