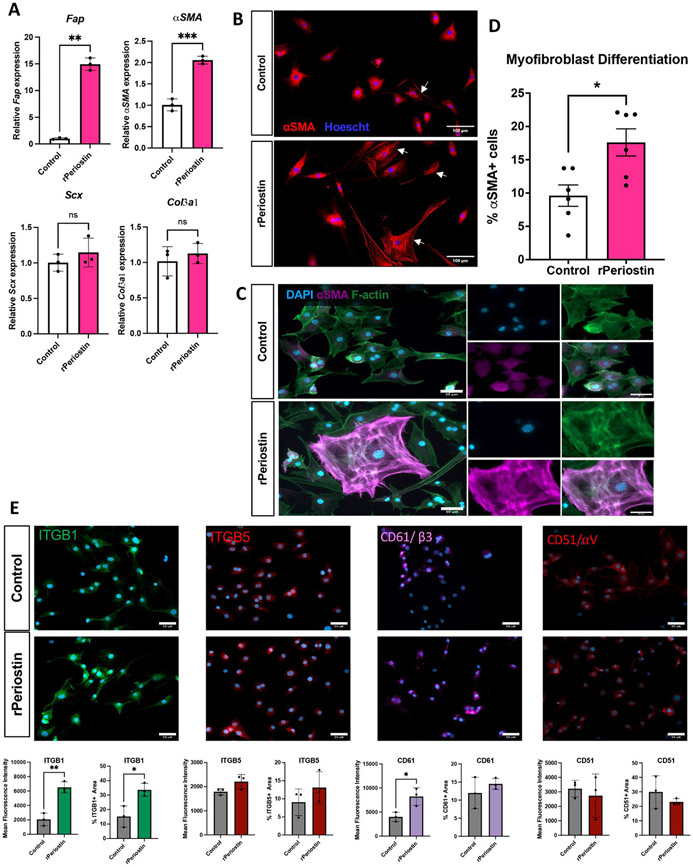
Figure 4. Postn matrix drive tenocyte activation and differentiation in vitro.
Primary murine tenocytes were seeded onto tissue culture plates coated with either collagen I alone (control), or collagen I with the addition of 10μg/mL recombinant Periostin (rPeriostin). (A) Changes in expression of genes associated with fibroblast activation (Fap), myofibroblast differentiation (αSMA), tenogenesis (Scx), and a healing-associated matrix (Col3a1) were assessed in tenocytes cultured on control and rPostn-coated plates. n=3 biological replicates (cells isolated from individual mice), with three technical replicates per biological sample. (B-D) The impact of rPeriostin on myofibroblast differentiation was assessed via immunostaining for αSMA (red), and nuclei were stained blue with Hoescht. The proportion of mature myofibroblasts (αSMA+ incorporated into F-actin stress fibers) were quantified relative to the overall cell count. n=6 biological replicates, with three technical replicates per biological sample. (E) Changes in expression area and mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of integrin subunits β1/ITGB1, β5/ITGB5, β3/CD61, αV/CD51 were quantified between rPeriostin and control cultures. n=3 biological replicates (cells isolated from individual mice), with three technical replicates per biological sample. (*) indicates p<0.05, (**) indicates p<0.01, (***) indicates p<0.001, (NS) indicates lack of statistical significance.