FIG. 5.
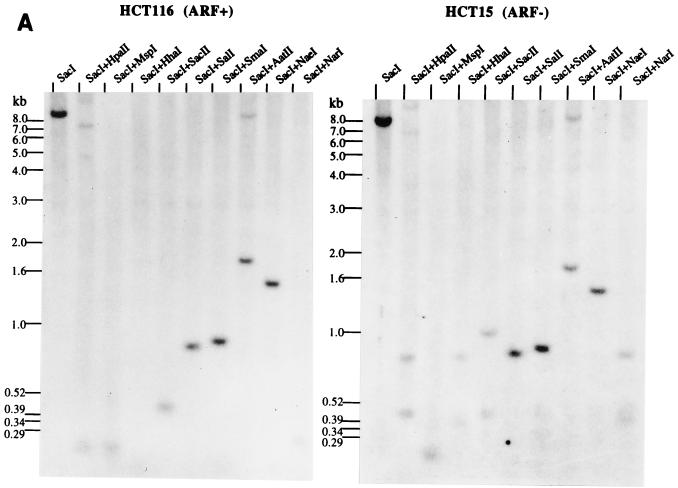
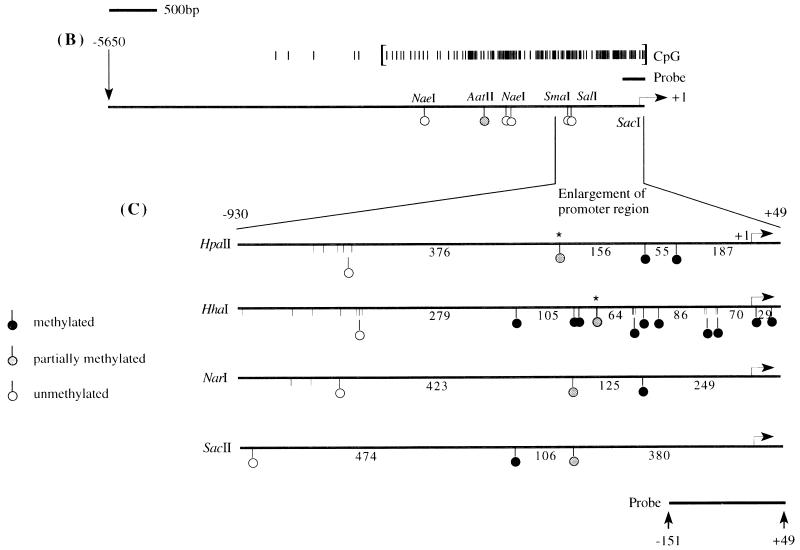
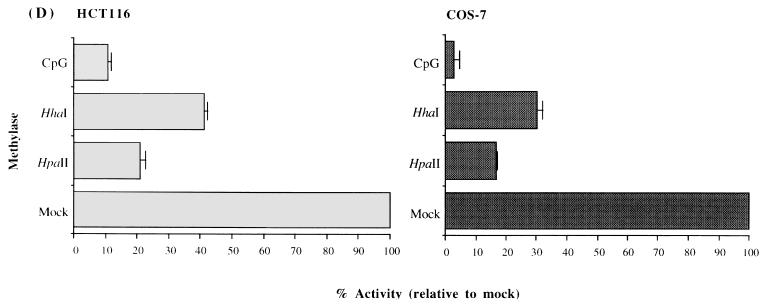
Methylation analysis of the ARF promoter. (A) Representative Southern blots after digestion of HCT116 and HCT15 genomic DNAs with the enzymes indicated and probing with the fragment shown in panels B and C. The presence of higher-molecular-weight bands in the HCT15 digests compared to the HCT116 digests is indicative of methylation. The low level of hybridization after digestion with enzymes like HpaII and HhaI is a result of the large number of such sites, creating many small restriction fragments which hybridize poorly. (B) Schematic of the location of several of the rare-cutting methylation-sensitive restriction enzyme sites, a CpG plot of the entire sequenced region, and the transcription start site (+1). Brackets in the CpG plot indicate the boundaries used for the calculation of CpG island status. The location of the probe is indicated by the thick bar, and the methylation status at the CpG sites analyzed by restriction digest is indicated by the lollipops. (C) Blowup of the region immediately adjacent to the ARF promoter (−930 to +49) and summary of the methylation status of CpG sites in this region as determined from blots in panel A for the HCT15 cell line. Asterisks indicate that these particular CpG sites, while partially methylated in HCT15 cells, were completely methylated in the LoVo cell line (not shown). The sizes of the fragments are indicated below the lines. A lollipop displaced below a group of restriction enzyme sites indicates that the sites were too close together to accurately determine which site was digested. (D) Analysis of the methylation sensitivity of the p(−151)19ARF promoter CAT construct after in vitro methylation and transfection into HCT116 or COS-7 cells. Results after treatment with the various methylases are presented as the mean percent activity relative to the mock-methylated control (no methylase) for triplicate transfections. Error bars represent the standard deviations.