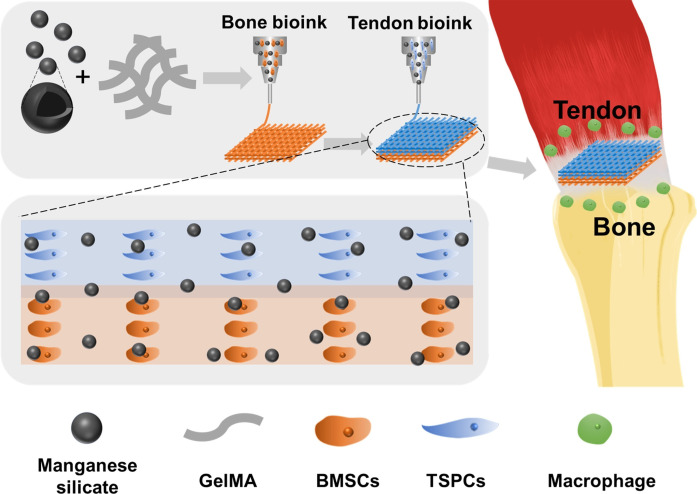
Fig. 1. Schematic illustration of the immunomodulatory multicellular scaffolds based on MS nanoparticles for integrated tendon-to-bone regeneration.
The multicellular scaffolds based on MS nanoparticles were fabricated through the spatial distribution of tendon stem/progenitor cells (TSPCs) and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) using 3D bioprinting, which achieved simulation of the tendon-to-bone interface. Moreover, MS nanoparticles were incorporated into the multicellular scaffolds for conferring immunomodulatory and integrated regenerative functions to the scaffolds. After being implanted into a rotator cuff tear (RCT), the multicellular scaffolds containing MS nanoparticles could induce the regeneration of tendon-to-bone interfaces in vivo.