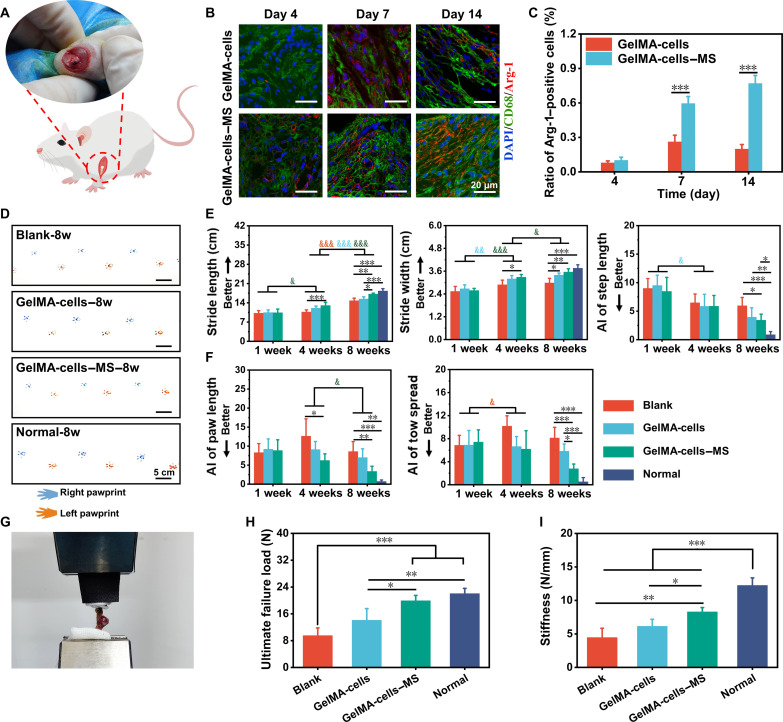
Fig. 4. The multicellular scaffolds based on MS nanoparticles achieved immunomodulation and induced functional restoration in rat RCT.
(A) The schematic diagram of rat RCT. (B) Representative immunofluorescence staining images of M2 polarization–related markers (Arg-1/CD68) in macrophages surrounding the implanted scaffolds on days 4, 7, and 14 after surgery. (C) Quantification of the number ratio of Arg-1 positive macrophages to total macrophages (n = 4). (D) Representative pawprints of different groups at 8 weeks postoperatively. Quantification of rat (E) spatial gait parameters (from left to right: stride length, stride width, and step length) and (F) paw parameters (from left to right: paw length and toe spread) in different groups at 1, 4, and 8 weeks after surgery (n = 4). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 (comparison of different groups at the same time point). &P < 0.05, &&P < 0.01, and &&&P < 0.001 (comparison of the same group at different time points. Red: Blank group; blue: GelMA-cells group; green: GelMA-cells-MS group). (G) The representative biomechanical test image of repaired rat rotator cuffs (n = 4). (H) The ultimate failure load and (I) stiffness of treated rotator cuffs in different groups at 8 weeks postoperatively (n = 4). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. The multicellular scaffolds based on MS nanoparticles polarized in vivo macrophages toward M2 phenotype and enhanced functional recovery in rat RCT.