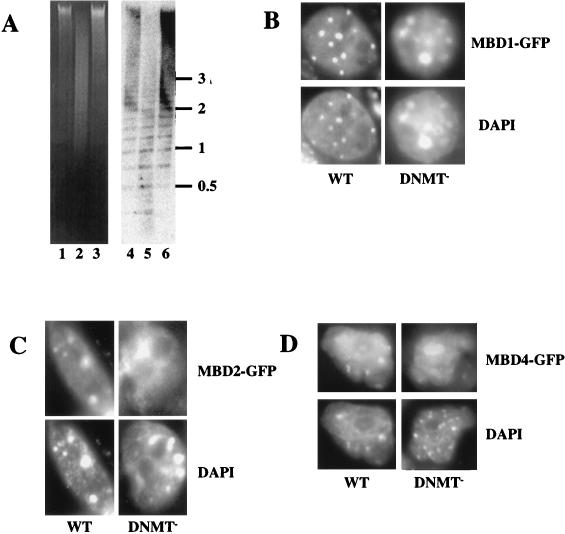
FIG. 5.
Binding of MBD proteins to methylated and hypomethylated genomes in vivo. (A) DNA from wild-type ES cells (lanes 1 and 4), DNMT mutant ES cells (lanes 2 and 5), and murine somatic cells (lanes 3 and 6) was digested with the methylation-sensitive restriction enzyme MaeII (Boehringer Mannheim) and electrophoresed on a 1% agarose gel. Lanes 1 to 3 show the ethidium bromide-stained gel, and lanes 4 to 6 show the gel blotted and probed with the 234-bp major satellite repeat monomer. (B to D) Localization of MBD-GFP fusion proteins in nuclei of ES cells. Either wild-type (WT) or DNMT-deficient (DNMT−) ES cells were transiently transfected with MBD1-GFP (B), MBD2-GFP (C), or MBD4-GFP (D) expression constructs. GFP fluorescence (upper panels) indicates the location of the MBD-fusion protein. DNA is visualized in the same nuclei by DAPI staining (lower panels), and major satellite is visible as intense spots of DAPI fluorescence. All fusion proteins are predominantly nuclear in all cells. MBD1-GFP colocalizes with major satellite in wild-type and mutant cells. MBD2-GFP and MBD4-GFP colocalize with major satellite in wild-type ES cells but fail to localize to major satellite in DNMT-deficient ES cell nuclei. Localization of MBD4-GFP to the nucleolus in DNMT-deficient ES cell nuclei was not observed consistently.