Figure 2.
Overview of data analysis using the TMCA-AAVseq protocol
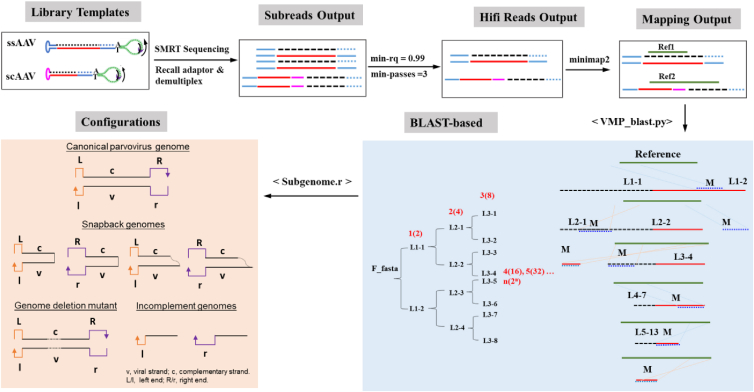
Starting from library preparations of SMRTbell DNA templates (as shown in Figure 1), through SMRT sequencing, to computational analysis with the <TMCA-AAVseq_Blast.py> script, which uses the BlastN algorithm for alignment. Iterative alignment refinement is depicted in the blue box, where the process extracts and aligns the best-matching segments for consecutive rounds of comparison. This iterative approach enables accurate mapping of subgenomic configurations, as indicated in the orange box, showcasing the primary configurations within the AAV vector genome library. For instance, with LOOP = 4, sequences from L1-1 to L3-8 are generated, along with their corresponding alignment results. These alignments allow for the HiFi reads to be precisely matched to reference loci. M denotes segments aligned in the current round, and L∗ represents segments not aligned. Unaligned segments L∗ are carried forward for alignment in subsequent rounds. This can continue recursively to provide a detailed overview of alignment status and subgenome configurations. scAAV genomes were not tested here.