Figure 3. Paneth Cell-Mediated Multiorgan Systemic Inflammation after Acute Kidney Injury.
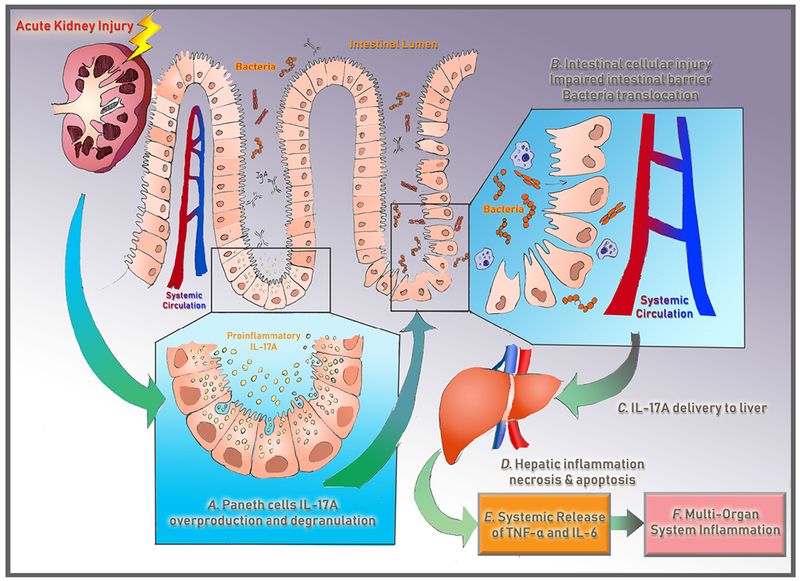
Recent experimental studies indicate that acute loss of kidney function causes small intestinal Paneth cells in the intestinal crypts to generate and degranulate proinflammatory IL-17-A into the intestinal lumen, which directly causes intestinal cellular injury and intestinal barrier breakdown. This allows for bacterial translocation and portal delivery of IL-17-A-containing macrophages, which causes hepatic injury and hepatic release of IL-6 and TNF-alpha into the circulation, leading to further hepatic and systemic inflammation. These studies highlight that acute kidney injury is not merely a bystander but can initiate a downward spiral triggering multi-organ failure and death.6
