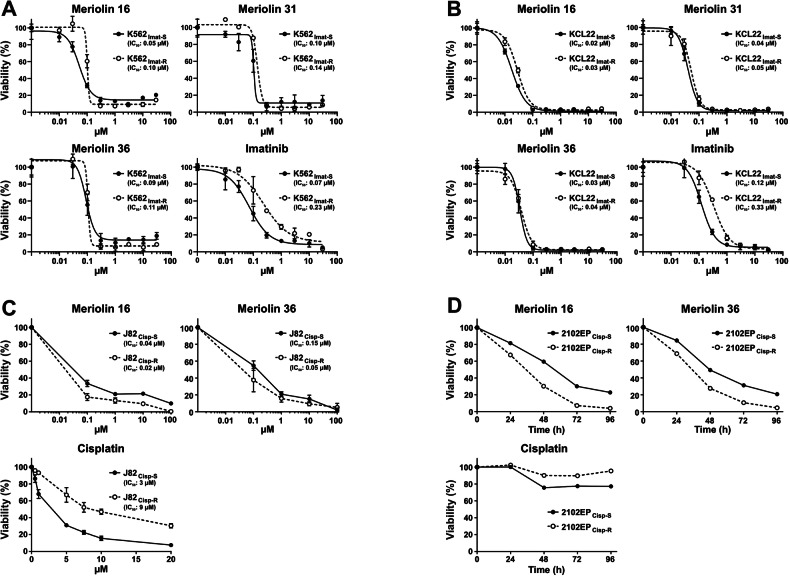
Fig. 7. Meriolin 16, 31, and 36 induce cytotoxicity in imatinib- and cisplatin-resistant tumor cell lines.
A, B Determination of cytotoxicity after 72 h treatment with meriolin 16 and 36 or imatinib in (A) imatinib-sensitive (K562 Imat-S) and -resistant (K562 Imat-R) K562 chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cells or B imatinib-sensitive (KCL22 Imat-S) and -resistant (KCL22 Imat-R) KCL22 CML cells. Cell viability was assessed by AlamarBlue® assay. Respective IC50 values are shown in parenthesis. Data shown are the mean ± SD from one (n = 1) experiment, performed in triplicates (n = 3). C Determination of cytotoxicity after 72 h treatment with meriolin 16 and 36 or cisplatin in cisplatin-sensitive (J82Cisp-S) and -resistant (J82Cisp-R) J82 urothelial carcinoma cells. Cell viability was assessed by AlamarBlue® assay. Respective IC50 values are shown in parenthesis. Data shown are the mean ± SD from three independent (n = 3) experiments, each performed in quadruplicate (n = 4). D Kinetics of cytotoxicity upon treatment with 1 µM cisplatin, meriolin 16 or 36 of cisplatin-sensitive (2102EPCisp-S) and -resistant (2102EPCisp-R) 2102EP germ cell tumor cells. Cell viability was assessed by XTT assay.