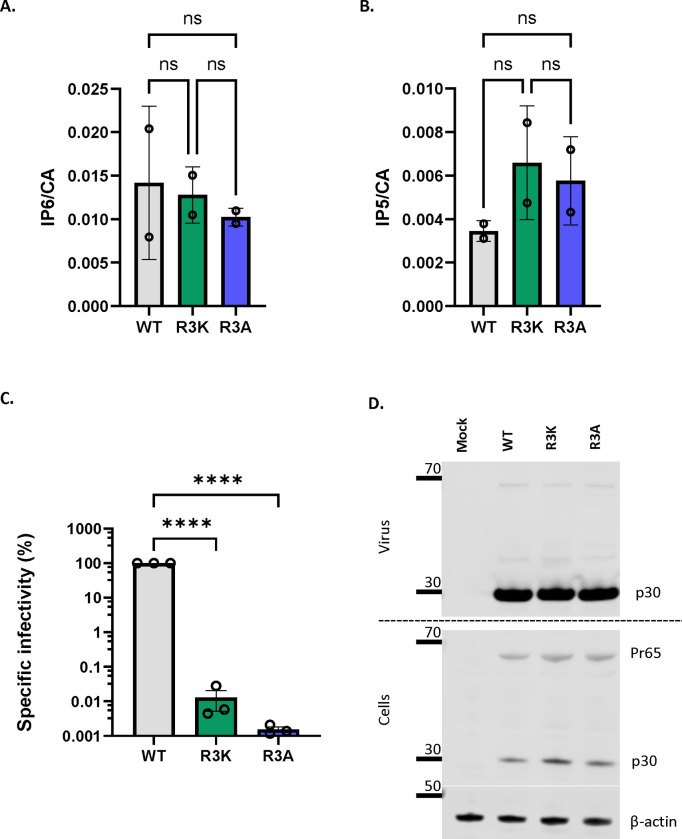
Figure 4: MLV R3 capsid mutants package IP6/5 but are non-infectious.
The bar graphs depict the packaging of A) IP6 and B) IP5 within WT, R3K, and R3A MLV viruses. The amount of IP6 and IP5 is normalized to the amount of capsid protein in each of the virus preparations. The graphs represent the mean ± SD from two independent experiments. C) A representative immunoblot against p30CA in the supernatant and cell lysates of cells transfected with either WT MLV or R3 capsid mutants of MLV (R3A and R3K). β-actin is used as a loading control. D) WT, R3A, and R3K MLV plasmids were co-transfected with pBabe-Luc into HEK 293T cells. Viruses produced by these transfected cells were used to infect HT1080mCAT cells, and lysates of these cells were assayed for luciferase activity. Specific infectivity was calculated by normalizing the luciferase values to the MLV p30CA levels (RLU/p30) indicative of the amount of virus in culture supernatants. The graphs represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Statistical significance is analyzed using one-way ANOVA. P values are indicated by *, ****P<0.0001, ns: not significant.