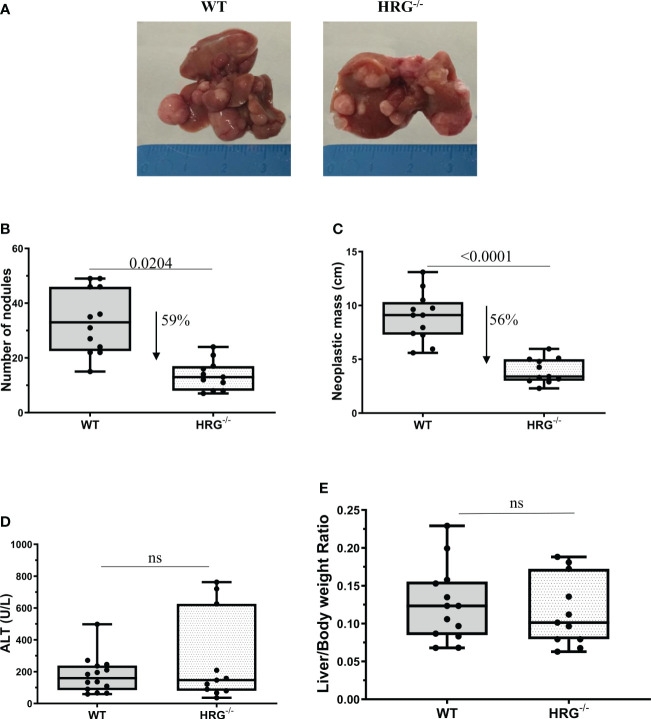
Figure 2.
HRG deletion significantly affects the development of experimental liver tumors. Reduction of number and of neoplastic mass measured in HCC tumors from 12 wild-type mice (WT) or 11 from HRG knock-out mice (HRG–/–) (A–C). The results are expressed as means ± SD. The boxes include the values within the 25th and 75th percentile, whereas the horizontal bars represent the medians. The extremities of the vertical bars (10th–90th percentile) comprise 80% of the values. Statistical differences were assessed by Student’s t-test (B, C). Parenchymal injury estimated by measuring the circulating levels of alanine (ALT) is reported in WT and HRG-/- mice (D). Liver/body weight ratio measured in WT and HRG-/- mice (E). The results are expressed as means ± SD. The boxes include the values within the 25th and 75th percentile, whereas the horizontal bars represent the medians. The extremities of the vertical bars (10th–90th percentile) comprise 80% of the values. Statistical differences were assessed by Student’s t-test or Mann–Whitney test for non-parametric values (D, E). ns, not significant.