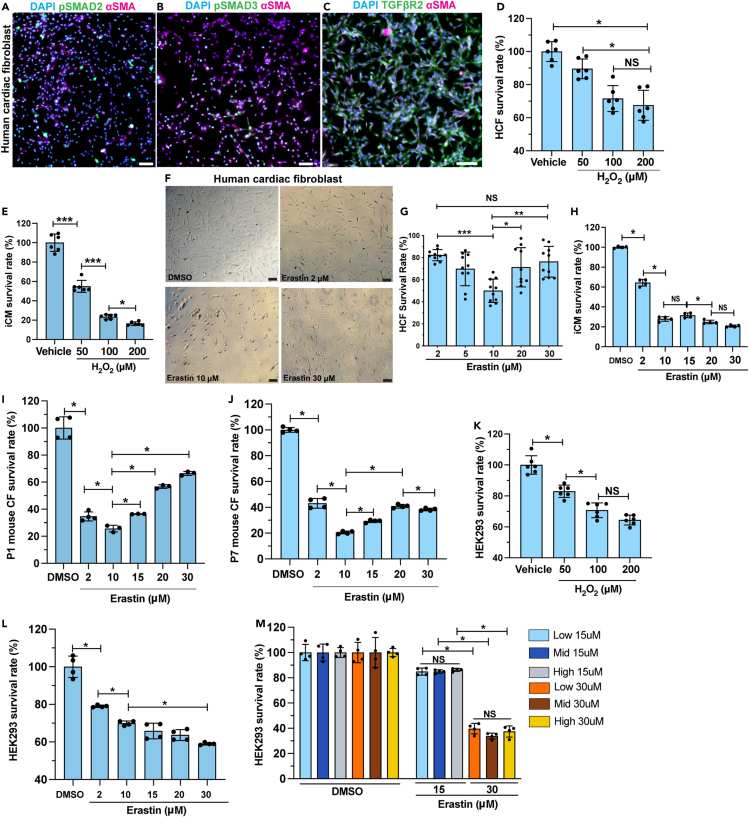
Figure 3.
Cardiac fibroblasts are resistant to ferroptosis
(A–C) HCFs were stained for pSMAD2 [green in (A)], pSMAD3 [green in (B)], and TGFβR2 [green in (C)], with αSMA (magenta) and DAPI (blue).
(D) Survival rate of HCFs after treatment with 50, 100, or 200 μM of H2O2, compared with vehicle (H2O).
(E) Survival rate of iCM after treatment with 50, 100, or 200 μM of H2O2, compared with vehicle (H2O).
(F and G) Brightfield of HCFs after erastin or DMSO treatment. Survival rate quantified in (G).
(H) Survival rate of iCMs after erastin treatment at 2, 10, 15, 20, or 30 μM, compared with DMSO control.
(I and J) Survival rate of primary mouse cardiac fibroblasts (CFs), prepared from P1 (I) and P7 (J) hearts, after erastin treatment.
(K) Survival rate of HEK293 cells after H2O2 or vehicle treatment.
(L) Survival rate of HEK293 cells treated with erastin at gradient concentration.
(M) Survival rate of HEK293 cells cultured at low, mid, and high density after erastin treatment at 15 or 30 μM, compared with DMSO groups. All bar graphs represent mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; NS, not significant by t test. Scale bar, 100 μm (A–C, E). See also Figure S3.