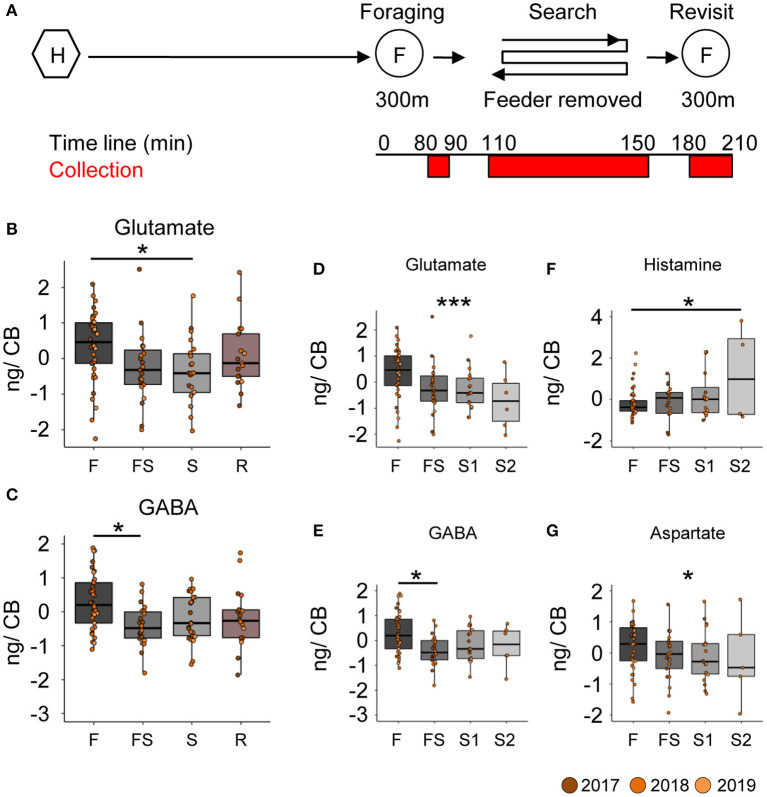
Figure 2.
Search behavior is correlated with reduced GABA and glutamate titers in the central brain. (A) Experimental design to collect foragers for mass spectrometric analysis of brain neurotransmitter titers. Individually marked foragers are allowed to visit the feeder at 300 m distance from the hive for an initial 1.5 h (foraging phase). The feeder is removed for 1 h (search phase) and reinstalled for 1 h (revisit phase). Foragers were captured at hive entrance during each behavior phase (marked red on experiment timeline). (B,C) Glutamate and GABA levels decrease in the central brain (CB) after bees experience a loss of their expected feeder. (D,E) A detailed look at the dynamics of change indicates that glutamate levels gradually but linearly decrease over increasing search trips (decrease by 112 ng per search flight, p-value = 0.001), but GABA levels only decrease post the first experience and stay that way. (F) Histamine (G) Aspartate (decrease by 87 ng per search flight, p-value = 0.031). The neurotransmitter values are scaled by the MS batch. *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001.