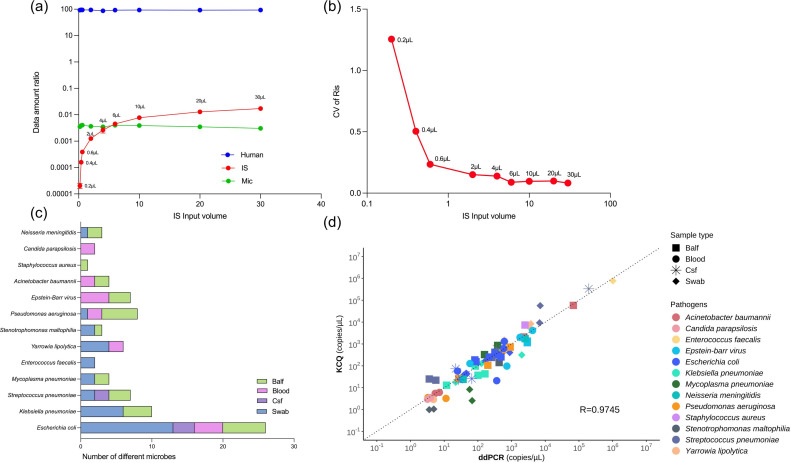
Fig. 5.
The quantitative capability of KCQ with Cclinical specimens. (a) The effect of IS input amount on the detection of microbial reads in a CFS specimen. (b) Effect of different IS input volumes on the detection of IS’s reads by KCQ. The data used for Cv calculation is the ratio of reads of IS between different gradients (Ris-n/Ris-n-1). (c) Thirty-six clinical specimens was quantitatively analyzedanalysed for the presence of microorganisms by KCQ and by ddPCR respectively. A total of 83 fragments were detected, including those commonly found pathogens such as Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Enterococcus faecalis, Yarrowia lipolytica, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Epstein-barr virus, Acinetobacter baumannii, Staphylococcus aureus, Candida parapsilosis, and Neisseria meningitidis among others. (d) Quantitative results were comparable by KCQ and ddPCR.