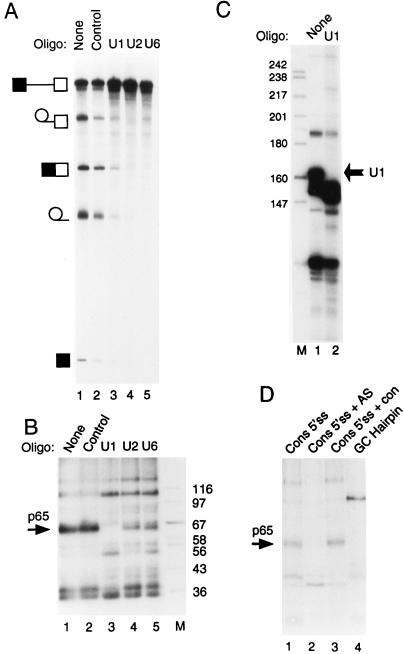
FIG. 6.
Cross-linking of p65 requires the 5′ end of U1 snRNA. (A) Splicing of GC+DX after oligonucleotide-directed RNase H destruction of snRNAs. Fifty percent HeLa nuclear extracts were incubated under normal splicing conditions in the presence of a DNA oligonucleotide and RNase H for 45 min. The transcript GC+DX was then added for a further 150 min of incubation. GC+DX was [32P]UTP labeled to low specific activity. Lanes: 1, no oligonucleotide-RNase H treatment; 2, control DNA oligonucleotide; 3, oligonucleotide against the 5′ end of U1 snRNA; 4, oligonucleotide against U2 snRNA; 5, oligonucleotide against U6 snRNA. Note that U2 and U6 targeting completely abolished splicing, while U1 destruction severely impaired splicing. (B) MB cross-linking of p65 after targeting of snRNAs. Fifty percent HeLa nuclear extracts were pretreated as in panel A. The transcript GC+DX [32P]GTP labeled to high specific activity was then added for a further 15 min of incubation. Lanes 1, no oligonucleotide-RNase H; 2, control oligonucleotide; 3, oligonucleotide against the 5′ end of U1 snRNA; 4, oligonucleotide against U2 snRNA; 5, oligonucleotide against U6 snRNA; M, protein size markers (kilodaltons). Note that p65 cross-linking is completely abolished after destruction of U1 snRNA (lane 3). (C) RNAs from untreated (lane 1) or a U1 oligonucleotide–RNase H-targeted extract (lane 2) were end labeled with 5′ [32P]pCp and then analyzed by electrophoresis and autoradiography. The intact U1 snRNA band in the untreated extract (indicated by the arrow) is undetectable (<1%) in the U1-targeted extract. (D) p65 does not cross-link to a nonspecific 5′ splice site duplex or to an RNA hairpin. RNAs were incubated with 40% HeLa nuclear extracts under normal splicing conditions for 15 min and then subjected to MB cross-linking. Lane 1, consensus 5′ splice site (Fig. 5). In lane 2, the consensus 5′ splice site was preannealed to a fivefold molar excess of unlabeled complementary RNA by heating at 65°C for 3 min and slow cooling to room temperature. In lane 3, the consensus 5′ splice site was incubated with a fivefold molar excess of a noncomplementary RNA at 65°C for 3 min and slowly cooled to room temperature. The nonradiolabeled RNA was transcribed from the same parental vector (pGEM 4Z) in the same direction, but lacking the 26-base 5′ splice site-containing insert. Lane 4, an RNA containing a 22-bp GC hairpin. Note that p65 cross-linking is inhibited by the 5′ splice site-RNA (compare lanes 1 and 2).