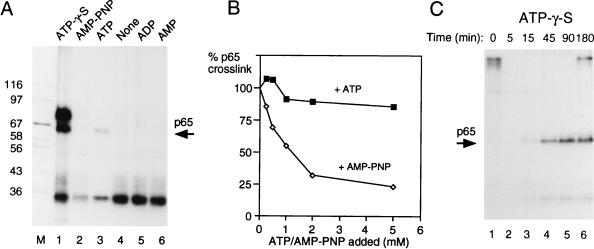
FIG. 8.
Cross-linking of p65 requires ATP hydrolysis. (A) MB cross-linking of p65 with GC+DX/XhoI in the presence of different ATP analogs. The RNA was incubated with 40% nuclear extract in the presence of different ATP analogs for 15 min and then subjected to MB cross-linking. Creatine phosphate was omitted in all samples. All of the ATP analogs and ATP were added to a 2 mM final concentration. Lanes: 1, ATP-γ-S; 2, AMP-PNP; 3, ATP; 4, no nucleotides added; 5, ADP; 6, AMP; M, protein size markers (kilodaltons). (B) Inhibition of p65 cross-linking by AMP-PNP. Labeled X23H RNA (5 ng) was incubated in 40% nuclear extract with 0.5 mM ATP, 20 mM creatine phosphate, and 2 mM MgCl2 at 30°C for 30 min before MB cross-linking. Reaction mixtures were supplemented at time zero with additional ATP or AMP-PNP along with an equimolar amount of MgCl2 before incubation. p65 cross-linking was quantitated by phosphorimager and is plotted as the percentage of cross-linking in the absence of additional nucleotide (i.e., in the presence of the basal 0.5 mM ATP). (C) Three-hour time course of MB cross-linking of GC+DX/BamHI transcript in the presence of 2 mM ATP-γ-S with no creatine phosphate. Splicing was carried out with 60% HeLa nuclear extracts. Note that p65 cross-linking persists over the time course.