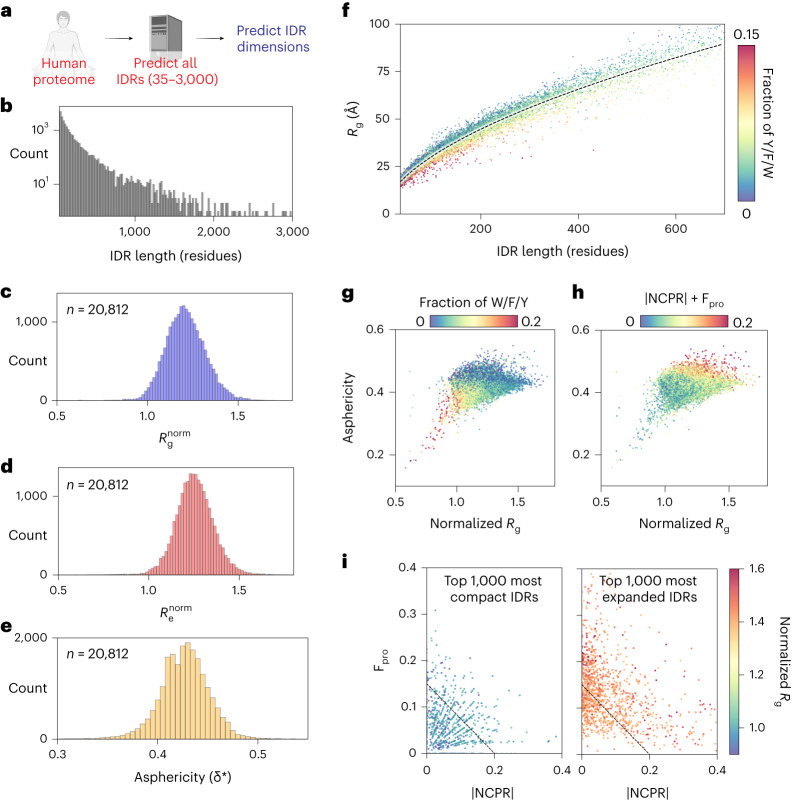
Fig. 4. Human proteome-wide biophysical characterization of predicted IDRs.
a, ALBATROSS was used to perform sequence-dependent ensemble predictions for all IDRs in the human proteome between 35 and 3,000 residues long. b, Histogram of all human IDRs ranging from 35 to 3,000 residues. There are just 12 IDRs longer than 3,000 residues in the human proteome. c, Normalized mean ALBATROSS Rg distribution for human IDRs. d, Normalized mean ALBATROSS Re distribution for human IDRs. e, Mean ALBATROSS asphericity distribution for IDRs in the human proteome. f, Mean ALBATROSS radius of gyration as a function sequence length. Individual data points are colored by the fraction of aromatic residues in the sequence. The dashed line represents the fitted scaling law, which reports an apparent scaling exponent of 0.56. Deviations above and below this line suggest sequence-specific expansion or compaction, respectively. g, Full distribution of human IDRs plotted in terms of the normalized radius of gyration and asphericity, colored by the fraction of aromatic residues. h, Full distribution of human IDRs plotted in terms of the normalized radius of gyration and asphericity, colored by the absolute NCPR plus the fraction of proline (Fpro) residues. i, Top 1,000 most compact (left) and top 1,000 most expanded (right) IDRs plotted in terms of the fraction of proline residues and absolute NCPR.