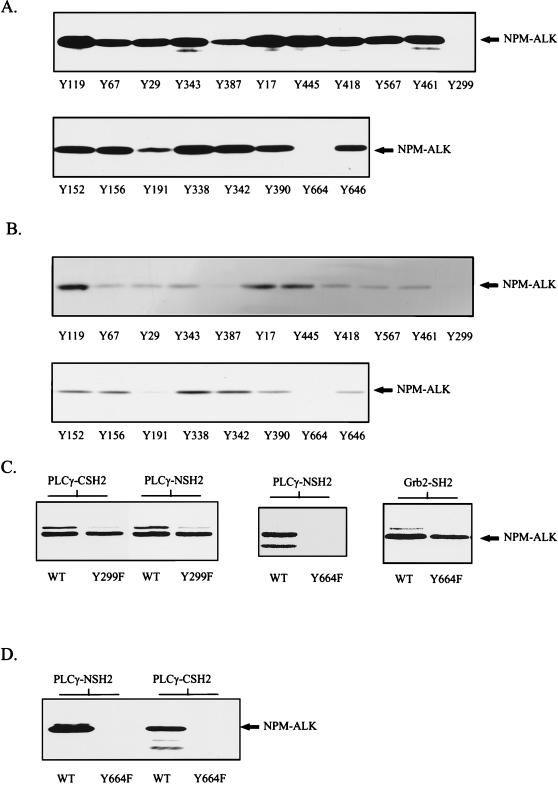
FIG. 4.
Phosphopeptide competition identifies Tyr664 in NPM-ALK as the binding site for PLC-γ. (A and B) Tyrosine-phosphorylated peptides corresponding to the putative autophosphorylation sites in NPM-ALK were synthesized with an SMPS 350 (Zinsser Analytik, Frankfurt, Germany) according to the method of Atherton and Sheppard (2). Tyrosine-phosphorylated peptides (200 μM) were incubated with ∼3 μg of GST fusion proteins of the PLC-γ N-terminal (A) or C-terminal (B) SH2 domain in lysis buffer for 1 h at 4°C. Cell lysates of 106 Karpas299 cells were then added to each binding reaction mixture, and mixtures were incubated for a further hour. Complexes were finally precipitated with glutathione-Sepharose, and samples were subjected to SDS–7.5% PAGE and analyzed by anti-ALK immunoblotting. Peptides Y299 and Y664 completely blocked in vitro association of NPM-ALK and the N-terminal and C-terminal SH2 domains of PLC-γ. (C) wt NPM-ALK (WT) and NPM-ALK mutants Y299F and Y664F were translated in vitro and labeled with [35S]methionine by the TNT coupled reticulocyte lysate system with T7 RNA polymerase. In vitro binding with the GST-SH2 domains of PLC-γ and Grb2 was performed as described in Material and Methods with ∼3 μg of GST fusion protein. Samples were resolved by SDS–7.5% PAGE and visualized by autoradiography. Y664, but not Y299, is essential for the binding of PLC-γ to NPM-ALK. (D) wt NPM-ALK (WT) and NPM-ALK(Y664F) sequences in pCDNA3 were stably transfected into Ba/F3 cells. Cell lysates were incubated with PLC-γ GST-NSH2 and PLC-γ GST-CSH2 and precipitated with glutathione-Sepharose, and samples were subjected to SDS–7.5% PAGE and analysis by anti-ALK immunoblotting.