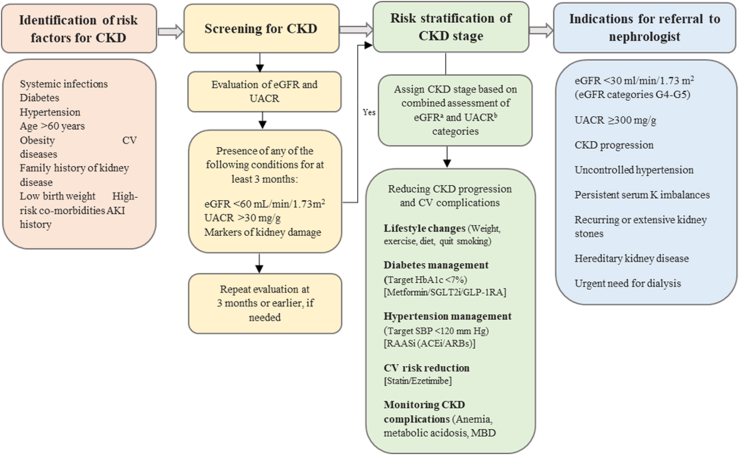
Figure 2.
Identification and referral pathway for the management of CKD. ACEi, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors; AKI, acute kidney injury; ARB, angiotensin receptor blockers; CKD, chronic kidney disease; CV, cardiovascular; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; GLP-1 RA, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; MBD, mineral bone diseases; RAASi, renin-angiotensin aldosterone system inhibitors; SBP, systolic blood pressure; SGLT2i, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors; UACR, urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio.
aeGFR categories in CKD classification G1: ≥90 ml/min per 1.73 m2, G2: 60–89 ml/min per 1.73 m2, G3a: 45–59 ml/min per 1.73 m2, G3b: 30–44 ml/min per 1.73 m2, G4: 15–29 ml/min per 1.73 m2 and G5: <15 ml/min per 1.73 m2 (kidney failure)
bUACR categories in CKD classification A1: <30 mg/g, A2: 30–300 mg/g, A3: >300 mg/g. Recreated with permission from Shlipak MG, Tummalapalli SL, Boulware LE, et al. The case for early identification and intervention of chronic kidney disease: conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Kidney Int. 2021;99(1):34-47. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2020.10.01256; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.