Figure 1.
Expression, assembly, and glycosylation of monoclonal IgG and different IgA antibodies from N. benthamiana plants
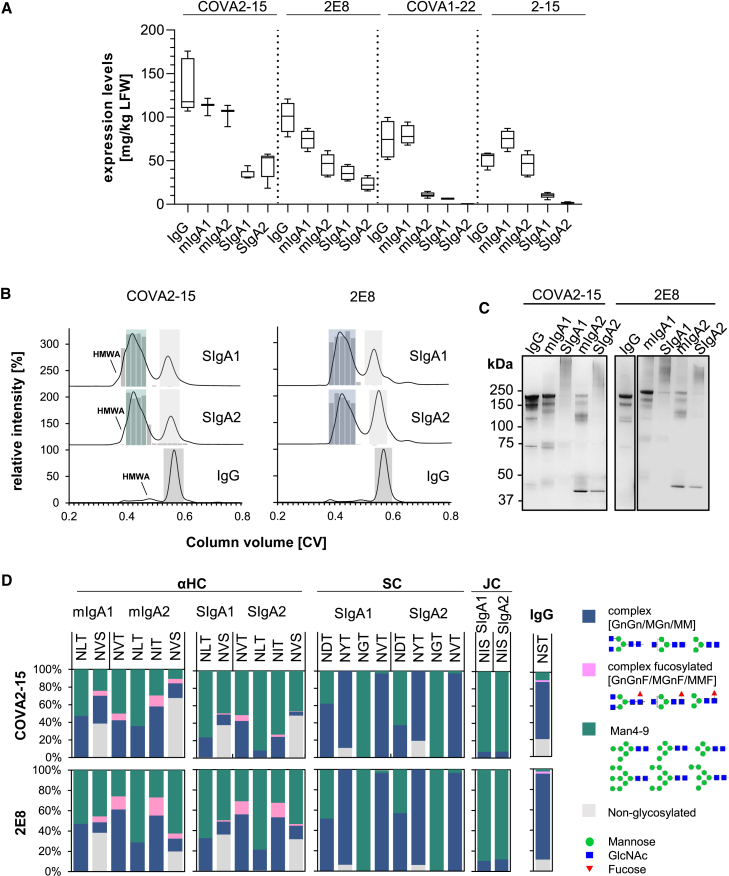
(A) IgG and monomeric and secretory IgA1 and IgA2 versions of 4 different mAbs recognizing the SARS-CoV-2 Spike proteins were transiently expressed in plants. Expression levels were quantified by sandwich ELISA in crude leaf extracts. The detection of monomeric IgA and IgG variants was with either HRP-labeled anti-kappa (COVA2-15) or anti-lambda light-chain (2E8, COVA1-22, 2–15) antibodies. SIgA antibodies were detected using anti-SC antibodies for all SIgA variants. Quantification data represent the mean of 2 technical repeats of 3 independent infiltrations of 3 plants each ± SD. (B) Normalized size-exclusion chromatograms of affinity-purified IgG, secretory IgA1, and secretory IgA2 of the COVA2-15 and 2E8 variants from infiltrated N. benthamiana ΔXT/FT leaves. Values were normalized based on the highest signal of each chromatogram. The ratio of functional secretory IgA to total IgA in each chromatography fraction was determined by antigen sandwich ELISA, and the relative amount of functional SIgA in each fraction is indicated by gray bars. Green, blue, and gray boxes indicated pooled fractions. (C) SDS-PAGE under nonreducing conditions of affinity and size-exclusion purified plant-produced IgG and monomeric and secretory IgA1/IgA2 of COVA2-15 and 2E8 visualized by Coomassie brilliant blue staining. (D) Site-specific N-glycosylation of purified mAbs. Bars represent the relative abundance (%) of glycoforms present at each glycosite of the heavy chains (HC; IgA1: sequon NLT and NVS, IgA2: NVT, NLT, NIT, and NVS, IgG1: NST), the SC (NTD, NYT, NGT, and NVT) and the JC (NIS). N-Glycans are abbreviated according to the ProGlycAn system (www.proglycan.com). The symbols for the monosaccharides are drawn according to the nomenclature from the Consortium for Functional Glycomics.